
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iron(II) bromide
| |
| Other names
Ferrous bromide
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.244 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FeBr2 | |
| Molar mass | 215.65 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow-brown solid |
| Density | 4.63 g cm−3, solid |
| Melting point | 684 °C (1,263 °F; 957 K) (anhydrous) 27 °C (Hexahydrate) |
| Boiling point | 934 °C (1,713 °F; 1,207 K) |
| 117 g / 100 ml | |
| Solubility in other solvents | THF, methanol, ethanol |
| +13,600·10−6 cm3/mol | |
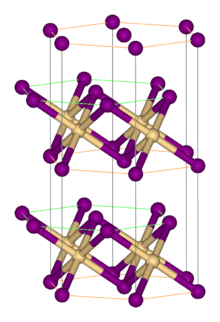
| Structure | |
| Rhombohedral, hP3, SpaceGroup = P-3m1, No. 164 | |
| octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
none |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Iron(II) fluoride Iron(II) chloride Iron(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Manganese(II) bromide Cobalt(II) bromide |
Related compounds
|
Vanadium(II) bromide Iron(III) bromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Iron(II) bromide refers to inorganic compounds with the chemical formula FeBr2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound (x = 0) is a yellow or brownish-colored paramagnetic solid. The tetrahydrate is also known, all being pale colored solids. They are common precursor to other iron compounds.