| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Iron(II) chloride
Iron dichloride | |||
| Other names
Ferrous chloride
Rokühnite | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.949 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| FeCl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 126.751 g/mol (anhydrous) 198.8102 g/mol (tetrahydrate) | ||
| Appearance | Tan solid (anhydrous) Pale green solid (di-tetrahydrate) | ||
| Density | 3.16 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.39 g/cm3 (dihydrate) 1.93 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate) | ||
| Melting point | 677 °C (1,251 °F; 950 K) (anhydrous) 120 °C (dihydrate) 105 °C (tetrahydrate) | ||
| Boiling point | 1,023 °C (1,873 °F; 1,296 K) (anhydrous) | ||
| 64.4 g/100 mL (10 °C), 68.5 g/100 mL (20 °C), 105.7 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |||
| Solubility in THF | Soluble | ||
| log P | −0.15 | ||
| +14750·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
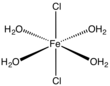
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Octahedral at Fe | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| B03AA05 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Iron (II) chloride MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Iron(II) fluoride Iron(II) bromide Iron(II) iodide | ||
Other cations
|
Cobalt(II) chloride Manganese(II) chloride Copper(II) chloride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0346". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).