| Ischemic colitis | |
|---|---|
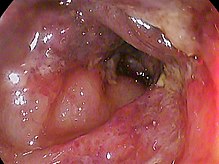 | |
| Ischemic colitis on the transverse colon of an 82 year old female | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
Ischemic colitis (also spelled ischaemic colitis) is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply (ischemia). Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater frequency in the elderly, and is the most common form of bowel ischemia.[1][2][3] Causes of the reduced blood flow can include changes in the systemic circulation (e.g. low blood pressure) or local factors such as constriction of blood vessels or a blood clot. In most cases, no specific cause can be identified.[4]
Ischemic colitis is usually suspected on the basis of the clinical setting, physical examination, and laboratory test results; the diagnosis can be confirmed by endoscopy or by using sigmoid or endoscopic placement of a visible light spectroscopic catheter (see Diagnosis). Ischemic colitis can span a wide spectrum of severity; most patients are treated supportively and recover fully, while a minority with very severe ischemia may develop sepsis and become critically,[5] sometimes fatally, ill.[6]
Patients with mild to moderate ischemic colitis are usually treated with IV fluids, analgesia, and bowel rest (that is, no food or water by mouth) until the symptoms resolve. Those with severe ischemia who develop complications such as sepsis, intestinal gangrene, or bowel perforation may require more aggressive interventions such as surgery and intensive care. Most patients make a full recovery; occasionally, after severe ischemia, patients may develop long-term complications such as a stricture[7] or chronic colitis.[8]
- ^ Higgins P, Davis K, Laine L (2004). "Systematic review: the epidemiology of ischaemic colitis" (PDF). Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 19 (7): 729–38. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01903.x. hdl:2027.42/74164. PMID 15043513. S2CID 9575677.
- ^ Brandt LJ, Boley SJ (2000). "AGA technical review on intestinal ischemia. American Gastrointestinal Association". Gastroenterology. 118 (5): 954–68. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(00)70183-1. PMID 10784596.
- ^ American Gastroenterological Association (2000). "American Gastroenterological Association Medical Position Statement: guidelines on intestinal ischemia". Gastroenterology. 118 (5): 951–3. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(00)70182-X. PMID 10784595. http://www.guideline.gov/summary/summary.aspx?ss=15&doc_id=3069&nbr=2295 Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
textp2332was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Medina C, Vilaseca J, Videla S, Fabra R, Armengol-Miro J, Malagelada J (2004). "Outcome of patients with ischemic colitis: review of fifty-three cases". Dis Colon Rectum. 47 (2): 180–4. doi:10.1007/s10350-003-0033-6. PMID 15043287. S2CID 24204840.
- ^ "Brighton marathon runner died from bowel failure". The Guardian newspaper. Press Association. 28 August 2013. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- ^ Simi M, Pietroletti R, Navarra L, Leardi S (1995). "Bowel stricture due to ischemic colitis: report of three cases requiring surgEsophageal dilatationery". Hepatogastroenterology. 42 (3): 279–81. PMID 7590579.
- ^ Cappell M (1998). "Intestinal (mesenteric) vasculopathy. II. Ischemic colitis and chronic mesenteric ischemia". Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 27 (4): 827–60, vi. doi:10.1016/S0889-8553(05)70034-0. PMID 9890115.