| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
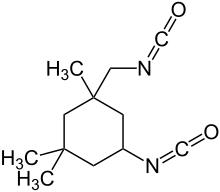
| IUPAC name
5-isocyanato-1-
| |
| Other names
IPDI
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.692 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 222.3 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless to slightly yellow liquid[1] |
| Odor | pungent[1] |
| Density | 1.062 g/cm3 @ 20 °C, liquid |
| Melting point | −60 °C (−76 °F; 213 K) |
| Boiling point | 158 °C (316 °F; 431 K) at 1.33 kPa |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0003 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) (PMCC) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.005 ppm (0.045 mg/m3) ST 0.02 ppm (0.180 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related isocyanates
|
Hexamethylene diisocyanate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for (with hexamethylene diisocyanate) only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000.[2] Aliphatic diisocyanates are used, not in the production of polyurethane foam, but in special applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation from ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft.[3]
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0356". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Randall, David; Lee, Steve (2002). The Polyurethanes Book. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-470-85041-8.
- ^ "ISOPHORONE DIISOCYANATE". Ataman Kimya (in Turkish). Retrieved 2023-12-20.