| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
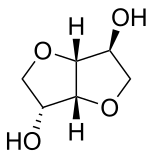
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3R,3aR,6S,6aR)-Hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan-3,6-diol | |
| Other names
D-Isosorbide; 1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol; 1,4-Dianhydrosorbitol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.449 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 146.142 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Highly hygroscopic white flakes |
| Density | 1.30 at 25 °C |
| Melting point | 62.5 to 63 °C (144.5 to 145.4 °F; 335.6 to 336.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) at 10 mmHg |
| in water (>850 g/L), alcohols and ketones | |
| Pharmacology | |
| None | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ismotic, Isobide, others |
| License data |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.449 |
Isosorbide is a bicyclic chemical compound from the group of diols and the oxygen-containing heterocycles, containing two fused furan rings. The starting material for isosorbide is D-sorbitol, which is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of D-glucose, which is in turn produced by hydrolysis of starch. Isosorbide is discussed as a plant-based platform chemical from which biodegradable derivatives of various functionality can be obtained.
In 2022, it was the 119th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5 million prescriptions.[1][2]
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Isosorbide Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.