This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2021) |
| Jing River | |
|---|---|
 Jing River in Jingyang County, close to where it flows into the Wei River | |
 | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | 34°28′10″N 109°04′02″E / 34.46944°N 109.06722°E |
| Length | 455.1 km (282.8 mi) |
| Basin size | 45,421 km2 (17,537 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Population | 9.48 million |
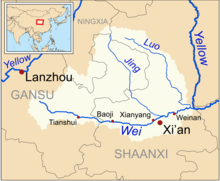
The Jing River (simplified Chinese: 泾河; traditional Chinese: 涇河) or Jing He (Pinyin: Jīng Hé), also called Jing Shui (simplified Chinese: 泾水; traditional Chinese: 涇水), is a tributary of the Wei River (Chinese: 渭河), which in turn is the largest tributary of the Yellow River.
The Jing River flows for 455.1 kilometres (282.8 mi), with a basin area of 45,421 square kilometres (17,537 sq mi).[1] The river's flow varies greatly throughout the year, and soil erosion causes serious problems in its basin. Summer floods cause the Jing to be laden with sediment; in the dry season, the river flows with relatively clear water.
The river flows through important farming areas, and its basin is inhabited by 9.5 million people.[1]
Water in the Jing River comes from Mount Liupan in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and flows through Gansu and Shaanxi, where it joins the Wei River in Gaoling District of Xi'an.[1] Other than its upper reaches, the river flows through loess landscape throughout its length.[2]
According to Chinese mythology a Dragon King ruled over the river. The Jing River basin is one of birthplaces of ancient Chinese civilization such as the Zhou dynasty.[3][4]
- ^ a b c Xu, Lihong; Shi, Zhongjie; Wang, Yanghui; Zhang, Shulan; Chu, Xinzheng; Yu, Pengtao; Xiong, Wei; Zuo, Haijun; Wang, Yunni (2015-11-15). "Spatiotemporal variation and driving forces of reference evapotranspiration in Jing River Basin, northwest China: Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Forces of Et o". Hydrological Processes. 29 (23): 4846–4862. doi:10.1002/hyp.10541. S2CID 131121601.
- ^ Chan, Kennis (2015-07-27). Environmental Engineering and Computer Application: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Computer Application (ICEECA 2014), Hong Kong, 25-26 December 2014. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-315-68538-0.
- ^ Gansu. Gansu People's Publishing House. 1984.
- ^ Field Trip Guide: Precambrian geology and mineral resources and seismology. Geological Publishing House. 1996. ISBN 978-7-116-02211-9.