| Kahayan River Sungai Kahayan | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Schwaner Mountains |
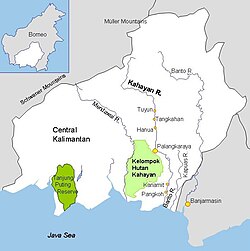
| • location | Central Kalimantan and West Kalimantan, Borneo |
| Mouth | Java Sea |
• location | Bapuju (Pulang Pisau Regency) |
• coordinates | 3°21′0″S 114°1′58″E / 3.35000°S 114.03278°E |
| Length | 658 km (409 mi) |
| Basin size | 15,500 km2 (6,000 sq mi)[1] 15,373 km2 (5,936 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Java Sea (near mouth) |
| • average | 1,178.4 m3/s (41,610 cu ft/s)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Palangkaraya (Basin size: 6,958 km2 (2,686 sq mi)[4] |
| • average | 771 m3/s (27,200 cu ft/s)[5] |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Kahayan basin (DAS320365)[6] |
The Kahayan River, or Great Dayak River, is the second largest river after the Barito River in Central Kalimantan, a province of Indonesia in Kalimantan – the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. With a total length of 658 km (409 mi) and with a drainage basin of 15,500 km2 (6,000 sq mi) in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. Mean annual discharge 1,178 m3/s (41,600 cu ft/s). The provincial capital Palangkaraya lies on the river. The main inhabitants are Dayaks, who practice slash-and-burn rice cultivation and pan for gold on the upper reaches. The lower Kayahan flows through a rich and unusual environment of peat swamp forests, which has been severely degraded by an unsuccessful program to convert a large part of the area into rice paddies, compounded by legal and illegal forestry.
- ^ Kevin, Telmer; Daniel, Stapper (November 2007). "Evaluating and Monitoring Small Scale Gold Mining and Mercury Use: Building a Knowledge-base with Satellite Imagery and Field Work".
- ^ Daniel, Stapper (2011). "Artisanal Gold Mining, Mercury and Sediment in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia" (PDF).
- ^ Kevin, Telmer; Daniel, Stapper (November 2007). "Evaluating and Monitoring Small Scale Gold Mining and Mercury Use: Building a Knowledge-base with Satellite Imagery and Field Work".
- ^ Daniel, Stapper (2011). "Artisanal Gold Mining, Mercury and Sediment in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia" (PDF).
- ^ Daniel, Stapper (2011). "Artisanal Gold Mining, Mercury and Sediment in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia" (PDF).
- ^ Hukum Online. "Keputusan Menteri Kehutanan No. SK.511/MENHUT-V/2011" (in Indonesian).

