This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2022) |
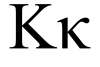 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diacritics and other symbols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


Kappa (/ˈkæpə/;[1] uppercase Κ, lowercase κ or cursive ϰ; Greek: κάππα, káppa) is the tenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless velar plosive IPA: [k] sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, Kʹ has a value of 20. It was derived from the Phoenician letter kaph ![]() . Letters that arose from kappa include the Roman K and Cyrillic К. The uppercase form is identical to the Latin K.
. Letters that arose from kappa include the Roman K and Cyrillic К. The uppercase form is identical to the Latin K.
Greek proper names and placenames containing kappa are often written in English with "c" due to the Romans' transliterations into the Latin alphabet: Constantinople, Corinth, Crete. All formal modern romanizations of Greek now use the letter "k", however.[citation needed]
The cursive form ϰ is generally a simple font variant of lower-case kappa, but it is encoded separately in Unicode for occasions where it is used as a separate symbol in math and science. In mathematics, the kappa curve is named after this letter; the tangents of this curve were first calculated by Isaac Barrow in the 17th century.
- ^ "kappa". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)