| Karelian | |
|---|---|
| karjala, karjalan kieli kard'al, kard'alan kiel' kariela, karielan kieli | |
| Native to | Russia, Finland |
| Region | Republic of Karelia, Tver Oblast (Tver Karelia) |
| Ethnicity | Karelians |
Native speakers | 9000 native speakers, 14,000 total (Russia) (2020)[1] 11,000 fluent speakers, 30,000 with some knowledge (Finland)[2][3] |
Uralic
| |
| Dialects | |
| Latin (Karelian alphabet) Cyrillic (in the past, 1820–1940, before the Latin script was officially adopted in 1989)[5] | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | krl |
| ISO 639-3 | krl |
| Glottolog | kare1335 |
| ELP | Karelian |
 | |
 Karelian is classified as "definitely endangered" by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger[10] | |
| People | Karelians |
|---|---|
| Language | Karelian; Livvi-Karelian |
| Country | Karelia |
Karelian (Karelian Proper and Livvi-Karelian: karjala, karjalan kieli; Ludian: kard'al, kard'alan kiel'; Tver Karelian: kariela, karielan kieli) is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as karjalaismurteet ("Karelian dialects") in Finland.[11] In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said to be able to speak the language.[12] There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland.[13] And around 30,000 have at least some knowledge of Karelian in Finland.[14]
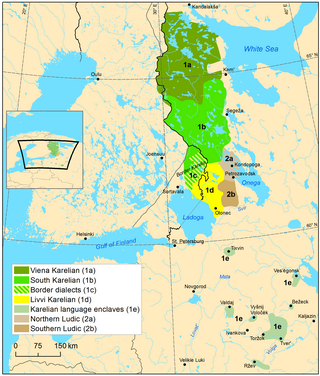
There is no single standard Karelian language, so the Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian and South Karelian (including the Tver enclave dialects)) and Olonets Karelian (Livvi Karelian). Ludic Karelian also appears in writing. All variants are written with the Latin-based Karelian alphabet, though the Cyrillic script has been used in the past. Each writer writes in Karelian according to their own dialectal form.
Based upon toponymic and historical evidence, a form of Karelian was also spoken among the extinct Bjarmians in the 15th century.[4]
- ^ "Rosstat — Vserossiyskaya perepis' naseleniya 2020" Росстат — Всероссийская перепись населения 2020 [Rosstat — All-Russian Population Census 2020]. rosstat.gov.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 2023-01-03.
- ^ "Karel'skiy yazyk" Карельский язык [Karelian] (in Russian).
- ^ "Karjala". Kotimaisten kielten keskus (in Finnish). Retrieved 2024-09-08.
- ^ a b Saarikivi, Janne. Substrata Uralica: Studies on Finno-Ugrian Substrate in Northern Russian Dialects (PhD thesis). Helsinki, Finland: University of Helsinki. ISBN 978-952-10-4519-6.
- ^ "Alphabet Karelian". Retrieved 2022-02-22.
- ^ Change in the regulation by the president of Finland about European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, 27.11.2009 (in Finnish)
- ^ "Законодательные акты – Правительство Республики Карелия". gov.karelia.ru. Archived from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2010-07-29.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
map1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
map2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Karelian in Russian Federation". UNESCO WAL. Retrieved 22 June 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
krl2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Росстат — Всероссийская перепись населения 2020". rosstat.gov.ru. Retrieved 2023-01-03.
- ^ "Karjalan kielen käytöstä saatiin runsaasti tietoa". Kotimaisten kielten keskus (in Finnish). Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ^ "Karjala". Kotimaisten kielten keskus (in Finnish). Retrieved 2024-09-08.