 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zaditor,[1] Alaway, others |
| Other names | ketotifen fumarate (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604033 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, eye drops, drug-eluting contact lenses |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60% |
| Protein binding | 75% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.348 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
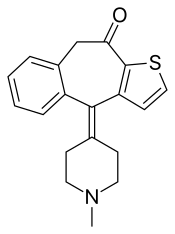
| Formula | C19H19NOS |
| Molar mass | 309.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ketotifen is an antihistamine medication and a mast cell stabilizer used to treat allergic conditions such as conjunctivitis, asthma, and urticaria (hives). Ketotifen is available in ophthalmic (eye drops or drug-eluting contact lenses) and oral (tablets or syrup) forms: the ophthalmic form relieves eye itchiness and irritation associated with seasonal allergies, while the oral form helps prevent systemic conditions such as asthma attacks and allergic reactions. In addition to treating allergies, ketotifen has shown efficacy in managing systemic mast cell diseases such as mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), which involve abnormal accumulation or activation of mast cells throughout the body. Ketotifen is also used for other allergic-type conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and food allergies.
Ketotifen acts by blocking the H1 histamine receptors, which are found on various cells in the body, such as smooth muscle, endothelium, and nerve cells. This blocking prevents the binding of histamine to these receptors and thus reduces the symptoms of histamine-mediated reactions, such as itching, sneezing, wheezing, and swelling.
Ketotifen also prevents the release of histamine and other inflammatory substances from immune cells (mast cells); this action helps reduce symptoms of conditions (including allergic conditions) by blocking the activation of these cells. In addition to its antihistaminic activity, ketotifen also functions as a leukotriene antagonist, which blocks inflammation-causing chemicals known as leukotrienes; it also acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor that regulates blood vessel dilation.
While well-tolerated, ketotifen can have side effects, including drowsiness, weight gain, dry mouth, irritability, increased nosebleeds when taken orally, and temporary burning or stinging sensations in the eyes when used in the ophthalmic form. Ketotifen has contraindications for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as acute porphyrias or epilepsy. Controversies surrounding ketotifen include its classification as a first-generation or second-generation antihistamine due to varying criteria of classification.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Zaditor FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Zaditen Product information". Health Canada. 22 October 2009. Archived from the original on 10 March 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ "Zaditor Product information". Health Canada. 22 October 2009. Archived from the original on 10 March 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ "Zaditen Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". emc. 13 October 2020. Archived from the original on 10 March 2024. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
dailymed-lenswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).