| Konkani | |
|---|---|
| कोंकणी · Konknni · ಕೊಂಕಣಿ · കൊങ്കണി · کونکنی[1] | |
 The word "Konkani" written in the official script of Devanagari[1] | |
| Pronunciation | [kõkɳi] (in the language itself), [kõkɵɳi] (anglicised) |
| Native to | India |
| Region | Southern and Western India (Konkan region)
|
| Ethnicity | Konkani |
Native speakers | 2.26 million (2011 census)[4] |
| Dialects |
|
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Karnataka Konkani Sahitya Academy and the Government of Goa[7] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | kok |
| ISO 639-3 | kok – inclusive codeIndividual codes: gom – Goan Konkaniknn – Maharashtrian Konkani |
| Glottolog | goan1235 Goan Konkanikonk1267 Konkan Marathi |
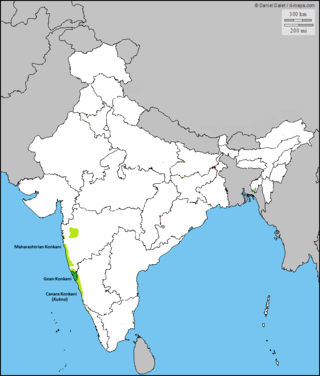 Distribution of native Konkani speakers in India | |
Konkani[note 3] (Devanagari: कोंकणी, Romi: Konknni, Kannada: ಕೊಂಕಣಿ, Malayalam: കൊങ്കണി, Perso-Arabic: کونکنی;[1] IAST: Kōṅkṇī, IPA: [kõkɳi]) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution,[9] and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is also spoken in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala,[10] Gujarat as well as Damaon, Diu & Silvassa.
Konkani is a member of the Southern Indo-Aryan language group. It retains elements of Vedic structures and shows similarities with both Western and Eastern Indo-Aryan languages.[11] The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 AD.[12]
There are many Konkani dialects spoken along and beyond the Konkan region, from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; most of which are only partially mutually intelligible with one another due to a lack of linguistic contact and exchanges with the standard and principal forms of Konkani. It is also spoken by migrants outside of the Konkan proper; in Nagpore, Surat, Cochin, Mangalore, Ahmedabad, Karachi, New Delhi etc.[13][14][15][16][17] Dialects such as Malvani, Chitpavani, Damani,[18] Koli & Aagri in Maharashtra; are threatened by language assimilation into the linguistic majority of non-Konkani states and territories of India.[19][20]
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
MadhaviSardesaiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Whiteley, Wilfred Howell (1974). Language in Kenya. Oxford University Press. p. 589.
- ^ Kurzon, Denis (2004). Where East looks West: success in English in Goa and on the Konkan Coast Volume 125 of Multilingual matters. Multilingual Matters. p. 158. ISBN 978-1-85359-673-5.
- ^ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues - 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ Kapoor, Subodh (10 April 2002). The Indian Encyclopaedia: La Behmen-Maheya. Cosmo Publications. ISBN 9788177552713 – via Google Books.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
goacom2049was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "The Goa Daman and Diu Official Language Act" (PDF). Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2009. Retrieved 5 March 2010.
- ^ "Konkani Language and History". Language Information Service. 6 July 2009. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Distribution of the 22 Scheduled Languages- India/ States/ Union Territories – 2001 Census".
- ^ Cardona, Jain, George, Dhanesh (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. pp. 1088 pages (see page:803–804). ISBN 9780415772945.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cardona, Jain, George, Dhanesh (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. pp. 1088 pages (see page:834). ISBN 978-0-415-77294-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Administrator. "Department of Tourism, Government of Goa, India - Language". goatourism.gov.in.
- ^ "Goan community celebrates World Goa Day". 14 September 2020.
- ^ "Goans mourn demise of Karachi GOA founder".
- ^ "Delhi Cabinet approves set-up of Konkani Academy in city: CM Kejriwal". 8 January 2021.
- ^ "About | the Gowd Saraswath Samaj". Archived from the original on 3 November 2022.
- ^ Parishad, Samyukta Maharashtra (1954). "Reorganization of States in India with Particular Reference to the Formation of Maharashtra: Being the Memorandum Submitted by the Samyukta Maharashtra Parishad to the States Reorganization Commission".
- ^ Frawley, William (May 2003). International Encyclopedia of Linguistics: 4-Volume Set. Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN 978-0-19-513977-8.
- ^ "'Konkanis to be blamed for lingo's precarious state' - Times of India". The Times of India. 22 August 2018. Retrieved 27 December 2020.
- ^ Menezes, Vivek (8 September 2017). "Konkani: a language in crisis". mint. Retrieved 27 December 2020.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).