44°6′N 146°42′E / 44.100°N 146.700°E
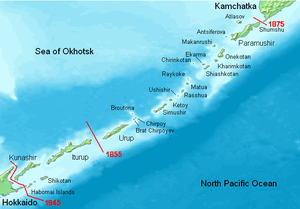


The Kuril Islands dispute, known as the Northern Territories dispute in Japan, is a territorial dispute between Japan and Russia over the ownership of the four southernmost Kuril Islands. The Kuril Islands are a chain of islands that stretch between the Japanese island of Hokkaido at their southern end and the Russian Kamchatka Peninsula at their northern end. The islands separate the Sea of Okhotsk from the Pacific Ocean. The four disputed islands, like other islands in the Kuril chain which are not in dispute, were unilaterally annexed by the Soviet Union following the Kuril Islands landing operation at the end of World War II. The disputed islands are under Russian administration as the South Kuril District and part of the Kuril District of the Sakhalin Oblast (Сахалинская область, Sakhalinskaya oblast). They are claimed by Japan, which refers to them as its Northern Territories or Southern Chishima, and considers them part of the Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture.
The islands in dispute are:
- Iturup (Russian: Итуруп)—Etorofu Island (Japanese: 択捉島)
- Kunashir (Russian: Кунашир)—Kunashiri Island (Japanese: 国後島)
- Shikotan (Russian: Шикотан)—Shikotan Island (Japanese: 色丹島)[1]
- Habomai Islands (Russian: острова Хабомаи ostrova Khabomai)—Habomai Islands (Japanese: 歯舞群島)[1]
The San Francisco Peace Treaty,[2] signed between the Allies and Japan in 1951, states that Japan renounces "all right, title and claim to the Kuril Islands", but does not explicitly recognize the Soviet Union's sovereignty over them.[3] Japan claims that at least some of the disputed islands are not a part of the Kuril Islands, and thus are not covered by the treaty.[4] Russia maintains that the Soviet Union's sovereignty over the islands was recognized in post-war agreements.[5] Japan and the Soviet Union ended their formal state of war with the Soviet–Japanese Joint Declaration of 1956 but did not sign a peace treaty. During talks leading to the joint declaration, the Soviet Union offered Japan the two smaller islands of Shikotan and the Habomai Islands in exchange for Japan renouncing all claims to the two bigger islands of Iturup and Kunashir, but Japan declined the offer. This disagreement between the two-island offer made by the Soviet Union and Japan's demand of regaining two bigger islands as well became the cornerstone for continuation of the dispute into the present day.[6]
- ^ a b In Russia Shikotan and Habomai Islands are grouped into the Lesser Kuril Chain (Russian: Малая Курильская гряда Malaya Kurilskaya gryada). See Seokwoo Lee, Towards a framework for the resolution of the territorial dispute over the Kurile Islands, Boundary and territory briefing, v. 3, no. 6, University of Durham, 2001; ISBN 1-897643-44-6; p. 14
- ^ Article 25 of The San Francisco Peace Treaty defines the Allied Forces as "the States at war with Japan, [...] provided that in each case the State concerned has signed and ratified the Treaty. [...] the present Treaty shall not confer any rights, titles or benefits on any State which is not an Allied Power as herein defined; nor shall any right, title or interest of Japan be deemed to be diminished or prejudiced by any provision of the Treaty in favor of a State which is not an Allied Power as so defined." The Allied powers were Australia, Canada, Ceylon, France, Indonesia, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, New Zealand, Pakistan, the Republic of the Philippines, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, and the United States of America. The Soviet Union refused to sign the treaty.
- ^ "Text of Gromyko's Statement on the Peace Treaty". The New York Times, page 26, September 9, 1951
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
clarkewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ О проблеме мирного договора в российско-японских отношениях [On the problem of a peace treaty in Russian-Japanese relations] (in Russian). Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 22 July 2005. Archived from the original on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ James D. J. Brown (2016). Japan, Russia and their Territorial Dispute: The Northern Delusion. Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 9781317272670.
In 1956, on the occasion of the restoration of bilateral diplomatic relations, Moscow officially stated that it was willing to transfer the two smaller islands to Japan following the conclusion of a peace treaty. As confirmed by Vladimir Putin in 2000 and again in 2012, this remains Moscow's position (Soejima and Komaki 2012). Japanese leaders, however, have consistently declined to accept this offer, drawing attention to the fact that Shikotan and Habomai represent only 7 percent of the disputed territory (Prime Minister Noda cited in Nihon Keizai Shinbun 2012). Despite the passage of much time and considerable diplomatic effort, the sides have essentially been unable to proceed beyond this impasse.