| Kurmali | |
|---|---|
| Panchpargania | |
| কুড়মালি, কুর্মালী कुड़मालि, कुरमालि କୁଡ଼ମାଲି पंचपरगनिया, পঞ্চপরগনিয়া | |
 ' Kuṛmāli ' written in Chisoi script | |
| Native to | India |
Native speakers | 555,695 (2011 census)[1][a] 619,689 (2001 census)[5] |
| Devanagari, Bengali, Odia, Chisoi[6] | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:kyw – Kudmalitdb – Panchpargania |
| Glottolog | kudm1238 Kudmalipanc1246 Panchpargania |
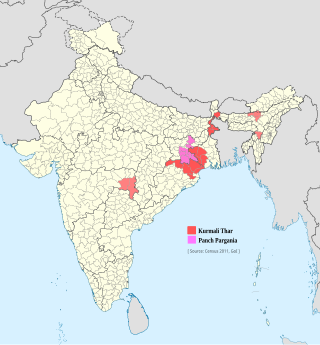 Distribution of Kurmali language in India | |
Kurmali or Kudmali (ISO: Kuṛmāli) is an Indo-Aryan language classified as belonging to the Bihari group of languages spoken in eastern India.[7][8][9] As a trade dialect, it is also known as Panchpargania (Bengali: পঞ্চপরগনিয়া), for the "five parganas" of the region it covers in Jharkhand. Kurmali language is spoken by around 550,000 people mainly in fringe regions of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal, also a sizeable population speak Kurmali in Assam tea valleys.[7] Kurmali is one of the demanded languages for enlisting in Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India.[10]
- ^ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2011" (PDF). www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ^ Ghosh 2020, pp. 439–501
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kurmali-Bengaliwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Laeequddin, Muhammad (1937). Census of Mayurbhanj State 1931 (PDF). Vol. I. Calcutta: Caledonin Printing Company. p. 241. JSTOR saoa.crl.25352830. OCLC 496724918.
The situation, however, is not the same with regard to the Kurmis. They had their own language, Kurmali, which they have abandoned in large numbers in favour of the peculiar form of Bengali spoken by them, which they brought with them into the State in the course of their migration through Manbhum and Midnapore.
- ^ "Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues: 2001". censusindia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 15 April 2022. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ^ "Proposal to Encode Chisoi in the Universal Character Set" (PDF). unicode.org. Retrieved 21 February 2022.
- ^ a b "Kudmali". Ethnologue. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- ^ Alam, Qaiser Zoha (1996). Language and Literature: Divers Indian Experiences. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. ISBN 978-81-7156-586-3.
- ^ Fayez, S. M., & Rajiv Ranjan Mahto. (2021). A Sociolinguistic Study of Kudmali in Jharkhand. Aligarh Journal of Linguistics, 11(ISSN: 2249-1511), 117–132.
- ^ "Constitutional provisions relating to Eighth Schedule" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).