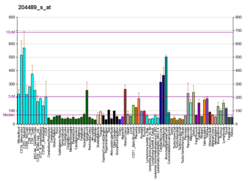
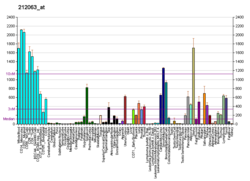
Kv7.1 (KvLQT1) is a potassium channel protein whose primary subunit in humans is encoded by the KCNQ1 gene.[5] It's mutation causes Long QT syndrome, Kv7.1 is a voltage and lipid-gated potassium channel present in the cell membranes of cardiac tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues. In the cardiac cells, Kv7.1 mediates the IKs (or slow delayed rectifying K+) current that contributes to the repolarization of the cell, terminating the cardiac action potential and thereby the heart's contraction. It is a member of the KCNQ family of potassium channels.
- ^ a b c ENSG00000053918 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000282076, ENSG00000053918 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000009545 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Jespersen T, Grunnet M, Olesen SP (2005). "The KCNQ1 potassium channel: from gene to physiological function". Physiology. 20 (6): 408–416. doi:10.1152/physiol.00031.2005. PMID 16287990.