| LASIK | |
|---|---|
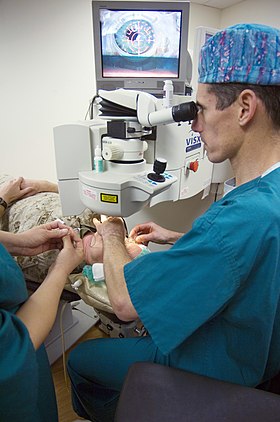 LASIK surgery using an excimer laser at US National Naval Medical Center Bethesda | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology, optometry |
| ICD-9-CM | 11.71 |
| MeSH | D020731 |
| MedlinePlus | 007018 |
LASIK or Lasik (/ˈleɪsɪk/; "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis"), commonly referred to as laser eye surgery or laser vision correction, is a type of refractive surgery for the correction of myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.[1] LASIK surgery is performed by an ophthalmologist who uses a femtosecond laser or a microkeratome to create a corneal flap to expose the corneal stroma and then an excimer laser to reshape the corneal stroma in order to improve visual acuity.[2][3]
LASIK is very similar to another surgical corrective procedure, photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), and LASEK. All represent advances over radial keratotomy in the surgical treatment of refractive errors of vision. For people with moderate to high myopia or thin corneas which cannot be treated with LASIK or PRK, the phakic intraocular lens is an alternative.[4][5]
As of 2018, roughly 9.5 million Americans have had LASIK[1][6] and, globally, between 1991 and 2016, more than 40 million procedures were performed.[7][8] However, the procedure seemed to be a declining option as of 2015.[9]
- ^ a b Rabin RC (11 June 2018). "Lasik's Risks Are Coming Into Sharper Focus – Some patients who undergo the eye surgery report a variety of side effects. They may persist for years, studies show". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- ^ "LASIK". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 13 June 2023. Archived from the original on 20 May 2024. Retrieved 15 August 2024.
- ^ Finn P (20 December 2012). "Medical Mystery: Preparation for surgery revealed cause of deteriorating eyesight". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 15 June 2018. Retrieved 2 September 2017.
- ^ Lovisolo CF, Reinstein DZ (November–December 2005). "Phakic intraocular lenses". Survey of Ophthalmology. 50 (6): 549–87. doi:10.1016/j.survophthal.2005.08.011. PMID 16263370.
- ^ Sanders DR, Vukich JA (May 2003). "Comparison of implantable contact lens and laser assisted in situ keratomileusis for moderate to high myopia". Cornea. 22 (4): 324–31. doi:10.1097/00003226-200305000-00009. PMID 12792475. S2CID 21142105.
- ^ Lindfield D, Poole T. "Nd:YAG Treatment of Epithelial Ingrowth". Cataract and Refractive Surgery Today. Archived from the original on 5 November 2013. Retrieved 12 September 2013.
- ^ Stodola E (1 April 2016). "LASIK worldwide". EyeWorld.org. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ Stuart A. "A Look at LASIK Past, Present and Future". EyeNet Magazine. Archived from the original on 31 July 2013. Retrieved 12 September 2013.
- ^ Corcoran KJ (July 2015). "Macroeconomic landscape of refractive surgery in the United States". Current Opinion in Ophthalmology. 26 (4): 249–54. doi:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000159. PMID 26058020. S2CID 11842503.