| LGM-25C Titan II | |
|---|---|
 An LGM-25C Titan intercontinental ballistic missile in silo, ready to launch | |
| Type | Intercontinental ballistic missile |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1962 to 1987 |
| Used by | United States |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Glenn L. Martin Company |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 155,000 kg (342,000 lb) |
| Length | 31.394 m (103.00 ft) |
| Diameter | 3.05 m (10.0 ft) |
| Warhead | W-53 9 Mt thermonuclear warhead |
Detonation mechanism | Air-burst or contact (surface) |
| Engine | Two-stage liquid-fueled rocket engines; first stage: LR-87; second stage: LR91 |
| Propellant | N2O4 / Aerozine 50 |
Guidance system | Inertial IBM ASC-15 |
Launch platform | Missile silo |
| Function | Launch vehicle |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Martin |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Cost per launch | $3.16 million in 1969[citation needed] |
| Size | |
| Height | 31.394 m (103.00 ft)(ICBM config) |
| Diameter | 3.05 m (10.0 ft) |
| Mass | 154,000 kg (340,000 lb) |
| Stages | 2 |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to LEO | |
| Mass | 3,600 kg (7,900 lb) |
| Payload to 100 km (62 mi) sub-orbital trajectory | |
| Mass | 3,700 kg (8,200 lb) |
| Payload to Polar LEO | |
| Mass | 2,177 kg (4,800 lb) |
| Payload to Escape | |
| Mass | 227 kg (500 lb) |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | Cape Canaveral LC-15, LC-16 & LC-19 Vandenberg Air Force Base LC-395 & SLC-4E/W |
| Total launches | 106 (81 suborbital) ICBM: 81 (suborbital) GLV: 12 23G: 13 |
| Success(es) | 101 (77 suborbital) ICBM: 77 (suborbital) GLV: 12 23G: 12 |
| Failure(s) | 5 (4 suborbital) ICBM: 4 (suborbital) 23G: 1 |
| First flight | 12 March 1962 |
| Last flight | 18 October 2003 |
| Type of passengers/cargo | Gemini (crewed) Clementine |
| First stage | |
| Powered by | 2 LR-87 |
| Maximum thrust | 1,900 kN (430,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 258 seconds (2.53 km/s) |
| Burn time | 156 s |
| Propellant | N2O4 / Aerozine 50 |
| Second stage | |
| Powered by | 1 LR91 |
| Maximum thrust | 445 kN (100,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 316 seconds (3.10 km/s) |
| Burn time | 180 s |
| Propellant | N2O4 / Aerozine 50 |



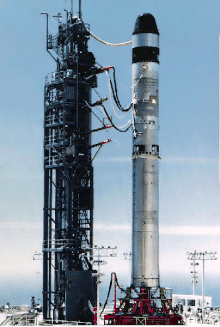
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space launch vehicle (these adaptations were designated Titan II GLV and Titan 23G) to carry payloads to Earth orbit for the United States Air Force (USAF), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Those payloads included the USAF Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP), NOAA weather satellites, and NASA's Gemini crewed space capsules. The modified Titan II SLVs (Space Launch Vehicles) were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, up until 2003.