| Lake Onega | |
|---|---|
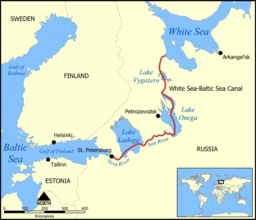 | |
| Coordinates | 61°41′26″N 35°39′20″E / 61.69056°N 35.65556°E |
| Primary inflows | 58 rivers (Shuya, Suna, Vodla, Vytegra, Andoma) |
| Primary outflows | Svir |
| Basin countries | Russia |
| Max. length | 245 km (152 mi) |
| Max. width | 91.6 km (56.9 mi) |
| Surface area | 9,891 km2 (3,819 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 30 m (98 ft) |
| Max. depth | 127 m (417 ft) |
| Water volume | 291 km3 (70 cu mi) |
| Surface elevation | 33 m (108 ft) |
| Islands | 1,369 (Kizhi Island) |
| Settlements | Kondopoga, Medvezhyegorsk, Petrozavodsk, Pindushi, Povenets |
 | |
Lake Onega (/oʊˈnɛɡə/; also known as Onego; Russian: Оне́жское о́зеро, romanized: Onezhskoe ozero, IPA: [ɐˈnʲɛʂskəɪ ˈozʲɪrə]; Finnish: Ääninen, Äänisjärvi; Livvi: Oniegujärvi; Veps: Änine, Änižjärv) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir.
There are about 1,650 islands on the lake. They include Kizhi, which hosts a historical complex of 89 Orthodox churches and other wooden structures of the 15th–20th centuries. The complex includes a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Kizhi Pogost. The eastern shores of the lake contain about 1,200 petroglyphs (rock engravings) dated to the 4th–2nd millennia BC, which have also been inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The major cities on the lake are Petrozavodsk, Kondopoga and Medvezhyegorsk.
