| Lake Tanganyika | |
|---|---|
| Ikiyaga ca Tanganyika (Kirundi) | |
 Lake Tanganyika from space, June 1985 | |
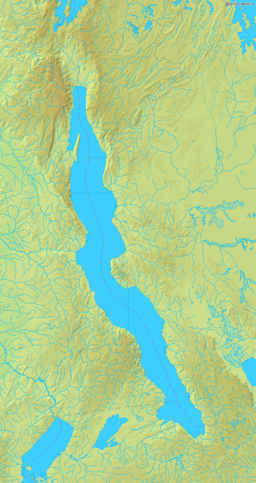 Lake Tanganyika map | |
| Coordinates | 6°06′S 29°30′E / 6.1°S 29.5°E |
| Lake type | Ancient lake, Rift Valley Lake |
| Primary inflows | Ruzizi River Malagarasi River Kalambo River |
| Primary outflows | Lukuga River |
| Catchment area | 231,000 km2 (89,000 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Burundi, DR Congo, Tanzania, and Zambia |
| Max. length | 673 km (418 mi) |
| Max. width | 72 km (45 mi) |
| Surface area | 32,900 km2 (12,700 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 570 m (1,870 ft) |
| Max. depth | 1,470 m (4,820 ft) |
| Water volume | 18,750 km3 (4,500 cu mi) |
| Residence time | 5500 years[1] |
| Shore length1 | 1,828 km (1,136 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 773 m (2,536 ft)[2] |
| Settlements | Kigoma, Tanzania Rukwa, Tanzania Kalemie, the DRC Bujumbura, Burundi Mpulungu, Zambia |
| References | [2] |
| Official name | Tanganyika |
| Designated | 2 February 2007 |
| Reference no. | 1671[3] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |

Lake Tanganyika (/ˌtæŋɡənˈjiːkə, -ɡæn-/ TANG-gən-YEE-kə, -gan-;[4] Kirundi: Ikiyaga ca Tanganyika) is an African Great Lake.[5] It is the second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia.[6][7] It is the world's longest freshwater lake.[6] The lake is shared among four countries—Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (the DRC), Burundi, and Zambia—with Tanzania (46%) and the DRC (40%) possessing the majority of the lake. It drains into the Congo River system and ultimately into the Atlantic Ocean.[citation needed]
- ^ Yohannes, Okbazghi (2008). Water resources and inter-riparian relations in the Nile basin. SUNY Press. p. 127.
- ^ a b "LAKE TANGANYIKA". www.ilec.or.jp. Archived from the original on 28 March 2008. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- ^ "Tanganyika". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Archived from the original on 27 April 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ Francis., Burton, Richard (1965). Burton and Lake Tanganyika. East African Literature Bureau. OCLC 180480726.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Lake Tanganyika". www.zambiatourism.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- ^ Lewis, R. (16 May 2010). "Brown Geologists Show Unprecedented Warming in Lake Tanganyika". Brown University. Archived from the original on 26 March 2017. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
