
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lead difluoride
plumbous fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.089 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PbF2 | |
| Molar mass | 245.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 8.445 g/cm3 (orthorhombic) 7.750 g/cm3 (cubic) |
| Melting point | 824 °C (1,515 °F; 1,097 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,293 °C (2,359 °F; 1,566 K) |
| 0.057 g/100 mL (0 °C) 0.0671 g/100 mL (20 °C)[1] | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
2.05 x 10−8 (20 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid and hydrochloric acid; insoluble in acetone and ammonia |
| −-58.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
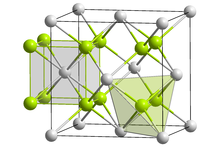
| Fluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3031 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lead(II) chloride Lead(II) bromide Lead(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Difluorocarbene Difluorosilylene Difluorogermylene Stannous fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lead(II) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula PbF2. It is a white solid. The compound is polymorphic, at ambient temperatures it exists in orthorhombic (PbCl2 type) form, while at high temperatures it is cubic (Fluorite type).[2]
- ^ NIST-data review 1980
- ^ Haines, J.; Léger, J. M.; Schulte, O. (1998-04-01). "High-pressure isosymmetric phase transition in orthorhombic lead fluoride". Physical Review B. 57 (13). American Physical Society (APS): 7551–7555. Bibcode:1998PhRvB..57.7551H. doi:10.1103/physrevb.57.7551. ISSN 0163-1829.