
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lead(II) oxide
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.880 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3288 2291 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PbO | |
| Molar mass | 223.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | red or yellow powder |
| Density | 9.53 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 888 °C (1,630 °F; 1,161 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,477 °C (2,691 °F; 1,750 K) |
| α-PbO: 0.0504 g/L (25 °C) β-PbO: 0.1065 g/L (25 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | insoluble in dilute alkalis, alcohol soluble in concentrated alkalis soluble in HCl, ammonium chloride |
| 4.20×10−5 cm3/mol | |
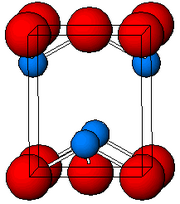
| Structure | |
| Tetragonal, tP4 | |
| P4/nmm, No. 129 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H332, H351, H360Df, H362, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P263, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P314, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LDLo (lowest published)
|
1400 mg/kg (dog, oral)[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0288 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lead(II) sulfide Lead selenide Lead telluride |
Other cations
|
Carbon monoxide Silicon monoxide Germanium monoxide Tin(II) oxide |
| Lead(II,IV) oxide Lead dioxide | |
Related compounds
|
Thallium(III) oxide Bismuth(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula PbO. PbO occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern applications for PbO are mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. It is an amphoteric oxide.[3]
- ^ Dorothy Greninger; Valerie Kollonitsch; Charles Howard Kline (1977). Lead Chemicals. International Lead Zinc Research Organization. p. 52.
- ^ "Lead compounds (as Pb)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
