| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lead(II) 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3-bis(olate) | |
| Other names
Lead 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3-diolate
Lead 2,4,6-trinitro-m-phenylene dioxide 1,3-Benzenediol, 2,4,6-trinitro-, lead(2+) salt (1:1) Lead tricinate Lead trinitroresorcinate Tricinat[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.703 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 0130 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6HN3O8Pb | |
| Molar mass | 450.288 g/mol |
| Density | 3.06 to 3.1 g cm−3 |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | High |
| Friction sensitivity | High |
| Detonation velocity | 5200 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H200, H302, H332, H360Df, H373, H410 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| 330 °C (626 °F; 603 K) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
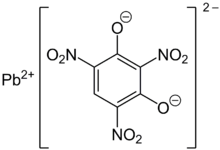
Lead styphnate (lead 2,4,6-trinitroresorcinate, C6HN3O8Pb ), whose name is derived from styphnic acid, is an explosive used as a component in primer and detonator mixtures for less sensitive secondary explosives. Lead styphnate is only slightly soluble in water and methanol.[3] Samples of lead styphnate vary in color from yellow to gold, orange, reddish-brown, to brown. Lead styphnate is known in various polymorphs, hydrates, and basic salts. Normal lead styphnate monohydrate, monobasic lead styphnate, tribasic lead styphnate dihydrate, and pentabasic lead styphnate dehydrate as well as α, β polymorphs of lead styphnate exist.
Lead styphnate forms six-sided crystals of the monohydrate and small rectangular crystals. Lead styphnate is particularly sensitive to fire and the discharge of static electricity. Long thin crystals are particularly sensitive. Lead styphnate does not react with other metals and is less sensitive to shock and friction than mercury fulminate or lead azide. It is stable in storage, even at elevated temperatures. As with other lead-containing compounds, lead styphnate is toxic owing to heavy metal poisoning.
- ^ ECHA, European Chemicals Agency "Support document for identification of lead styphnate as a substance of very high concern because of its CMR properties" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-22. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ^ GHS: GESTIS 490561
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
