 | |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
lithium cobalt(III) oxide
| |
| Other names
lithium cobaltite
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.135 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| LiCoO 2 | |
| Molar mass | 97.87 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark blue or bluish-gray crystalline solid |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
harmful |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H317, H350, H360 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P272, P280, P281, P302+P352, P308+P313, P321, P333+P313, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
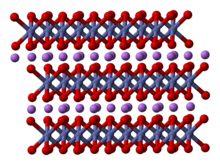
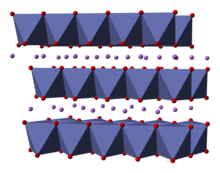
Lithium cobalt oxide, sometimes called lithium cobaltate[2] or lithium cobaltite,[3] is a chemical compound with formula LiCoO
2. The cobalt atoms are formally in the +3 oxidation state, hence the IUPAC name lithium cobalt(III) oxide.
Lithium cobalt oxide is a dark blue or bluish-gray crystalline solid,[4] and is commonly used in the positive electrodes of lithium-ion batteries.
- ^ 442704 - Lithium cobalt(III) oxide (2012-09-14). "Sigma-Aldrich product page". Sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 2013-01-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ A. L. Emelina, M. A. Bykov, M. L. Kovba, B. M. Senyavin, E. V. Golubina (2011), "Thermochemical properties of lithium cobaltate". Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry, volume 85, issue 3, pages 357–363; doi:10.1134/S0036024411030071
- ^ Ondřej Jankovský, Jan Kovařík, Jindřich Leitner, Květoslav Růžička, David Sedmidubský (2016) "Thermodynamic properties of stoichiometric lithium cobaltite LiCoO2". Thermochimica Acta, volume 634, pages 26-30. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2016.04.018
- ^ LinYi Gelon New Battery Materials Co., Ltd, "Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) for lithium ion battery ". Catalog entry, accessed on 2018-04-10,