| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium N-(propan-2-yl)propan-2-aminide | |
| Other names
LDA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.721 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
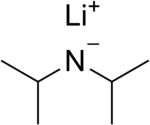
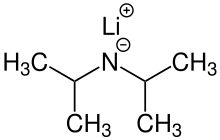
| LiN(CH(CH3)2)2 | |
| Molar mass | 107.1233 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless solid |
| Density | 0.79 g/cm3 |
| Reacts with water | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 36 (THF)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Superbases |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula LiN(CH(CH3)2)2. It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature. It is a colorless solid, but is usually generated and observed only in solution. It was first prepared by Hamell and Levine in 1950 along with several other hindered lithium diorganylamides to effect the deprotonation of esters at the α position without attack of the carbonyl group.[2]
- ^ Evans pKa Table
- ^ Hamell, Matthew; Levine, Robert (1950). "Condensations Effected by the Alkali Amides. IV. The Reactions of Esters with Lithium Amide and Certain Substituted Lithium Amides1". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 15: 162–168. doi:10.1021/jo01147a026.