
| |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium fluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.229 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| LiF | |
| Molar mass | 25.939(2) g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder or colorless hygroscopic crystals |
| Density | 2.635 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 845 °C (1,553 °F; 1,118 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,676 °C (3,049 °F; 1,949 K) |
| 0.127 g/(100 mL) (18 °C) 0.134 g/(100 mL) (25 °C) | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
1.84×10−3[1] |
| Solubility | soluble in HF insoluble in alcohol |
| −10.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3915 |
| Structure | |
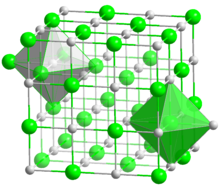
| Face-centered cubic | |
a = 403.51 pm
| |
| Linear | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
1.507 J/(g·K) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
35.73 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-616 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H315, H319, H335[2] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
143 mg/kg (oral, rat)[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lithium chloride Lithium bromide Lithium iodide Lithium astatide |
Other cations
|
Sodium fluoride Potassium fluoride Rubidium fluoride Caesium fluoride Francium fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiF. It is a colorless solid that transitions to white with decreasing crystal size. Its structure is analogous to that of sodium chloride, but it is much less soluble in water. It is mainly used as a component of molten salts.[4] Partly because Li and F are both light elements, and partly because F2 is highly reactive, formation of LiF from the elements releases one of the highest energies per mass of reactants, second only to that of BeO.
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–188. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ "Lithium fluoride - Product Specification Sheet". Sigma-Aldrich. Merck KGaA. Retrieved 1 Sep 2019.
- ^ "Lithium fluoride". Toxnet. NLM. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 10 Aug 2014.
- ^ Aigueperse J, Mollard P, Devilliers D, et al. (2005). "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_307. ISBN 9783527303854.
