
| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium imide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li2NH | |
| Molar mass | 28.897 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.48 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium imide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li2NH. This white solid can be formed by a reaction between lithium amide and lithium hydride.[1]
- LiNH2 + LiH → Li2NH + H2
The product is light-sensitive and can undergo disproportionation to lithium amide and characteristically red lithium nitride.
- 2 Li2NH → LiNH2 + Li3N
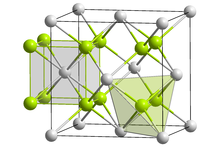
Lithium imide is thought to have a simple face-centered cubic structure with a Fm3m space group; with N-H bond distances of 0.82(6) Å and a H–N–H bond angle of 109.5°, giving it a similar structure to lithium amide.[2][3]
Lithium imide is strongly basic and deprotonates even some extremely weak acids such as methane and ammonia, due to the very localized negative charge on the nitrogen, which carries two formal charges. It has uses in organic and organometallic chemistry. It has been investigated as a material for hydrogen storage.[1]
- ^ a b Ichikawa, Takayuki; Hanada, Nobuko; Isobe, Shigehito; Leng, Haiyan; Fujii, Hironobu (June 2004). "Mechanism of Novel Reaction from LiNH2 and LiH to Li2NH and H2 as a Promising Hydrogen Storage System". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 108 (23): 7887–7892. doi:10.1021/jp049968y.
- ^ Ohoyama, Kenji; Nakamori, Yuko; Orimo, Shin-ichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi (15 January 2005). "Revised Crystal Structure Model of Li2NH by Neutron Powder Diffraction". Journal of the Physical Society of Japan. 74 (1): 483–487. arXiv:cond-mat/0406025. Bibcode:2005JPSJ...74..483O. doi:10.1143/JPSJ.74.483. S2CID 94983390.
- ^ Noritake, T.; Nozaki, H.; Aoki, M.; Towata, S.; Kitahara, G.; Nakamori, Y.; Orimo, S. (May 2005). "Crystal structure and charge density analysis of Li2NH by synchrotron X-ray diffraction". Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 393 (1–2): 264–268. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.09.063.