 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.711 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
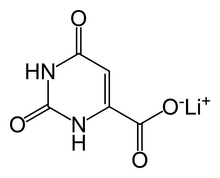
| Formula | C5H3LiN2O4 |
| Molar mass | 162.03 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lithium orotate (C5H3LiN2O4) is a salt of orotic acid and lithium. It is available as the monohydrate, LiC5H3N2O4·H2O.[1] In this compound, lithium is non-covalently bound to an orotate ion, rather than to a carbonate or other ion, and like other salts, dissolves in solution to produce free lithium ions. It is marketed as a dietary supplement, though it has been researched minimally between 1973–1986 to treat certain medical conditions, such as alcoholism[2] and Alzheimer's disease.
While lithium orotate is capable of providing lithium to the body,[3] like lithium carbonate and other lithium salts, there are no systematic reviews supporting the efficacy of lithium orotate and it is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of any medical condition.
- ^ Bach I, Kumberger O, Schmidbaur H (1990). "Orotate complexes. Synthesis and crystal structure of lithium orotate( - I) monohydrate and magnesium bis[ orotate( - I)] octahydrate". Chemische Berichte. 123 (12): 2267–2271. doi:10.1002/cber.19901231207.
- ^ Sartori HE (1986). "Lithium orotate in the treatment of alcoholism and related conditions". Alcohol. 3 (2): 97–100. doi:10.1016/0741-8329(86)90018-2. PMID 3718672.
- ^ Pacholko AG, Bekar LK (2021). "Lithium orotate: A superior option for lithium therapy?". Brain and Behavior. 11 (4): e2262. doi:10.1002/brb3.2262. PMC 8413749. PMID 34196467.