
| |

| |
 | |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium oxide
| |
| Other names
Lithia
Kickerite Dilithium Monoxide Dilithium Oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.823 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li 2O | |
| Molar mass | 29.88 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 2.013 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,438 °C (2,620 °F; 1,711 K) |
| Boiling point | 2,600 °C (4,710 °F; 2,870 K) |
| Reacts to form LiOH | |
| log P | 9.23 |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.644 [1] |
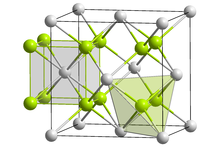
| Structure | |
| Antifluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Tetrahedral (Li+); cubic (O2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
1.8105 J/g K or 54.1 J/mol K |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
37.89 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-20.01 kJ/g or -595.8 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
-562.1 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive, reacts violently with water |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lithium sulfide Lithium selenide Lithium telluride Lithium polonide |
Other cations
|
Sodium oxide Potassium oxide Rubidium oxide Caesium oxide |
| Lithium peroxide Lithium superoxide | |
Related compounds
|
Lithium hydroxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium oxide (Li
2O) or lithia is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a white solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For example, the Li2O content of the principal lithium mineral spodumene (LiAlSi2O6) is 8.03%.[2]
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
