 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gamanil, Lomont, Tymelyt, others |
| Other names | Lopramine; DB-2182; Leo-460; WHR-2908A[1][2][3][4] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 7%[5] |
| Protein binding | 99%[6] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (via cytochrome P450, including CYP2D6)[7] |
| Metabolites | Desipramine (major) |
| Elimination half-life | Up to 5 hours;[1] 12–24 hours (active metabolites) |
| Excretion | Urine, feces (mostly as metabolites) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.254 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
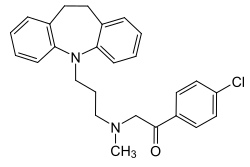
| Formula | C26H27ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 418.97 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lofepramine, sold under the brand names Gamanil, Lomont, and Tymelyt among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used to treat depression.[7][3][8] The TCAs are so named as they share the common property of having three rings in their chemical structure. Like most TCAs lofepramine is believed to work in relieving depression by increasing concentrations of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin in the synapse, by inhibiting their reuptake.[7] It is usually considered a third-generation TCA, as unlike the first- and second-generation TCAs it is relatively safe in overdose and has milder and less frequent side effects.[9]
Lofepramine is not available in the United States, Canada, Australia or New Zealand, although it is available in Ireland, Japan, South Africa and the United Kingdom, among other countries.[1]
- ^ a b c "Lofepramine Hydrochloride". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. The Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Elks2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 614–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Drugs.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lancaster SG, Gonzalez JP (February 1989). "Lofepramine. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in depressive illness". Drugs. 37 (2): 123–140. doi:10.2165/00003495-198937020-00003. PMID 2649353. S2CID 195693275.
- ^ "Lofepramine 70mg tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Merck Serono. 18 November 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
EMCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Leonard BE (October 1987). "A comparison of the pharmacological properties of the novel tricyclic antidepressant lofepramine with its major metabolite, desipramine: a review". International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2 (4): 281–297. doi:10.1097/00004850-198710000-00001. PMID 2891742.
- ^ "SAFC Commercial Life Science Products & Services | Sigma-Aldrich". Safcglobal.com. 2015-05-12. Retrieved 2016-02-24.