| Long-tailed ground roller | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult in Mangily, Madagascar | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Coraciiformes |
| Family: | Brachypteraciidae |
| Genus: | Uratelornis Rothschild, 1895 |
| Species: | U. chimaera
|
| Binomial name | |
| Uratelornis chimaera Rothschild, 1895
| |
| |
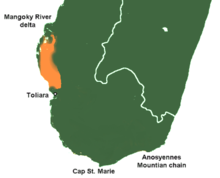
| Distribution (orange) in southern Madagascar | |
The long-tailed ground roller (Uratelornis chimaera) is a species of bird in the ground roller family Brachypteraciidae, placed in the monotypic genus Uratelornis. Endemic to arid spiny forests near the coast in southwestern Madagascar, this ground roller occurs at extremely low population densities throughout its habitat. This species requires shade and a deep layer of leaves on the ground, and it is absent from parts of the spiny forest lacking these features. It has no recognized subspecies, and its closest relative is the scaly ground roller. The long-tailed ground roller is the only ground roller to definitively display sexual dimorphism (differences in plumage or size between sexes). It is a medium-sized bird with a plump silhouette and a long tail. The upperparts are dark brown with black streaks while the underparts are light gray. The white throat is framed by black malar stripes and a black breastband, and a white stripe is present at the base of the bill. Sky-blue feathers are visible at the edge of the wings and the tail. Calls are rarely made outside the breeding season, though multiple courtship calls are made.
These ground rollers feed primarily on invertebrates, including ants, beetles, butterflies, and worms, which they find by searching through deep leaf litter or by remaining still and watching attentively. The ground roller primarily runs through its habitat on its strong legs, as its wings are relatively weak. It is a monogamous species, and it defends a territory during the breeding season of October to February. It digs a tunnel in the sand, at the end of which is a wider chamber where it makes its nest out of leaves and earthy pellets. Two to four eggs are laid. After the chicks fledge, the birds continue living in family groups until at least February before dispersing more widely across the scrubland.
This bird is classified as vulnerable by the IUCN and is threatened by habitat destruction. Since the arid, spiny forests in which it lives are not protected by the Malagasy government, it is losing habitat to slash-and-burn agriculture, charcoal collection, and logging. It is also hunted by the native peoples of Madagascar.
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Uratelornis chimaera". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22682969A92970628. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22682969A92970628.en. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
