 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ABT-378 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a602015 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Protein binding | 98-99% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 6 hours |
| Excretion | Mostly fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.281.362 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
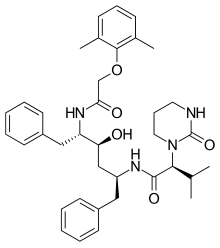
| Formula | C37H48N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 628.814 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir).[1]
It was patented in 1995 and approved for medical use in 2000.[2] Considered now as second-line therapy in the West, it is still prescribed in LMIC, especially among children living with HIV. Lopinavir and ritonavir can be taken as a tablet or an oral solution, a preferred option in children. In the early stages of COVID-19 pandemics, lopinavir was repurposed against the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the hope of disturbing its protease activity.[3]
- ^ "FDA Approved Drug Products: Kaletra". Retrieved 30 April 2004.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 510. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Perazzolo, Simone; Zhu; Lin, Weixian; Nguyen, Alexander; Ho, Rodney JY (2021). "Systems and Clinical Pharmacology of COVID-19 Therapeutic Candidates: A Clinical and Translational Medicine Perspective". J Pharm Sci. 110 (3): 1002–1017. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2020.11.019. PMC 7689305. PMID 33248057.