 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Noctamid, Loramet, others |
| Other names | Methyllorazepam; Methyl-lorazepam; N-Methyllorazepam; Ro 5-5516 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous[1] |
| Drug class | Benzodiazepine |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 10–12 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.546 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
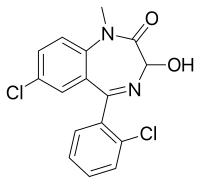
| Formula | C16H12Cl2N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 335.18 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lormetazepam, sold under the brand name Noctamid among others, is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy[3] benzodiazepine derivative and temazepam analogue.[4] It possesses hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
It was patented in 1961 and came into medical use in 1980.[5] Lormetazepam is not approved for sale in the United States or Canada. It is licensed in the UK as 0.5 and 1 mg tablets for short-term treatment (2–4 weeks) of moderately severe insomnia. It is licensed in the Netherlands as 1 and 2 mg tablets, under the brand names Loramet and Noctamid and as generic, available from several manufacturers. It is sold in Poland as Noctofer. It is also sold in France as generic as 1 and 2mg tablets, with a maximum prescription duration of 4 weeks. A Dutch analysis stated that lormetazepam could be suitable to be included in drug prescribing formularies, although zolpidem, zopiclone, and temazepam appear better.[6]
- ^ Horowski R (August 2020). "Dependence liability of lormetazepam: are all benzodiazepines equal? The case of the new i.v. lormetazepam for anesthetic procedures". Journal of Neural Transmission. 127 (8): 1107–1115. doi:10.1007/s00702-020-02209-8. PMC 8823007. PMID 32468272.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Doenicke A, Dorow R, Täuber U (December 1991). "[The pharmacokinetics of lormetazepam following cimetidine]" [The pharmacokinetics of lormetazepam following cimetidine]. Der Anaesthesist (in German). 40 (12): 675–679. PMID 1685875.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
analogueswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 537. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Janknegt R, van der Kuy A, Declerck G, Idzikowski C (August 1996). "Hypnotics. Drug selection by means of the System of Objectified Judgement Analysis (SOJA) method". PharmacoEconomics. 10 (2): 152–163. doi:10.2165/00019053-199610020-00007. PMID 10163418.