 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /loʊˈsɑːrtən/ |
| Trade names | Cozaar, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695008 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Angiotensin II receptor antagonist |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–35% |
| Protein binding | 99.7% (primarily albumin) |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C9, CYP3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5–2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney 13–25%, bile duct 50–60% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.110.555 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
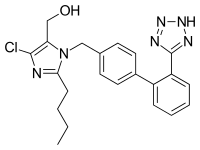
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| Molar mass | 422.92 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Losartan, sold under the brand name Cozaar among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).[4] It is in the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) family of medication, and is considered protective of the kidneys. Besides hypertension, it is also used in diabetic kidney disease, heart failure, and left ventricular enlargement.[4] It comes as a tablet that is taken by mouth.[4] It may be used alone or in addition to other blood pressure medication.[4] Up to six weeks may be required for the full effects to occur.[4]
Common adverse effects include muscle cramps, stuffy nose, dizziness, cough, high blood potassium, and anemia.[4] Severe adverse effects may include angioedema, low blood pressure, and kidney problems.[4] Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby.[4][1] Use is not recommended during breastfeeding.[1] It works by blocking angiotensin II.[4]
Losartan was patented in 1986, and approved for medical use in the United States in 1995.[4][5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[7] In 2022, it was the eighth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 53 million prescriptions.[8][9] A version combined with hydrochlorothiazide is available[4] which, in 2022, was the 75th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8 million prescriptions.[8][10]
- ^ a b c "Losartan (Cozaar) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Cozaar FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Losartan Potassium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 470. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 127. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ a b "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Losartan Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Hydrochlorothiazide; Losartan Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.