 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Amitiza |
| Other names | RU-0211 SPI-0211 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607034 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Negligible |
| Protein binding | 94% |
| Metabolism | Extensive, CYP not involved |
| Elimination half-life | Unknown (lubiprostone) 0.9–1.4 hours (main metabolite) |
| Excretion | Kidney (60%) and fecal (30%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
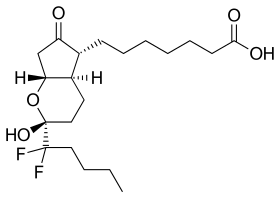
| Formula | C20H32F2O5 |
| Molar mass | 390.468 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lubiprostone, sold under the brand name Amitiza among others, is a medication used in the management of chronic idiopathic constipation, predominantly irritable bowel syndrome-associated constipation in women and opioid-induced constipation. The drug is owned by Mallinckrodt and is marketed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
The drug was developed by Sucampo Pharmaceuticals and approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2006.[2][3][4] It was recommended for use in the UK by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in July 2014.[5] Health Canada approved the drug in 2015.[6] Lubiprostone received approval from the Food and Drug Administration in 2008, to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C),[7] and in 2013, for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation in adults with chronic noncancer pain.[4] It is available as a generic medication.[8]
- ^ "Health Canada New Drug Authorizations: 2015 Highlights". Health Canada. 4 May 2016. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ "FDA Approves New Type of Drug To Treat Constipation in Adults". The Wall Street Journal. February 1, 2006.
- ^ "Highlights of Prescribing Information" (PDF). FDA. 2020.
- ^ a b Webster LR, Brewer RP, Lichtlen P, Losch-Beridon T, Mareya S, Wang M (June 2018). "Efficacy of Lubiprostone for the Treatment of Opioid-Induced Constipation, Analyzed by Opioid Class". Pain Medicine. 19 (6): 1195–1205. doi:10.1093/pm/pnx212. PMID 29897589.
- ^ "Final appraisal determination: Lubiprostone for treating chronic idiopathic constipation". National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. June 2014.
- ^ "Health Canada New Drug Authorizations: 2015 Highlights". Health Canada. 2016-05-04.
- ^ "In the news: FDA approves one drug for irritable bowel syndrome but suspends another". Harvard Health. 2008-08-01.
- ^ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.