| Lymphangiectasia | |
|---|---|
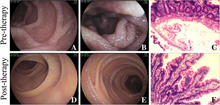 | |
| Lymphangiectasia shown on enteroscopy. | |
| Specialty | Angiology |
Lymphangiectasia, also known as "lymphangiectasis",[1] is a pathologic dilation of lymph vessels.[2] When it occurs in the intestines it is known as intestinal lymphangiectasia, colloquially recognized as Waldmann's disease in cases where there is no secondary cause.[3] The primary defect lies in the inability of the lymphatic system to adequately drain lymph, resulting in its subsequent accumulation and leakage into the intestinal lumen.[3] This condition, first described by Waldmann in 1961, is typically diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.[3] However, it can also manifest in adults, exhibiting a broad spectrum of clinical symptoms.[3]
- ^ "lymphangiectasia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ McGavin/ Zachary (2007), Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease
- ^ a b c d Waldmann, T.A.; Steinfeld, J.L.; Dutcher, T.F.; Davidson, J.D.; Gordon, R.S. (2008). "The Role of the Gastrointestinal System in "Idiopathic Hypoproteinemia"". Gastroenterology. 41 (3): 197–207. doi:10.1016/s0016-5085(19)35130-3. ISSN 0016-5085.