This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2024) |
| Lymphatic malformation or Lymphangioma | |
|---|---|
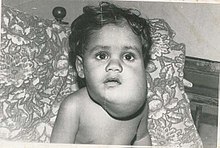 | |
| Lymphatic malformation of the neck | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Lymphatic malformations are benign slow-flow type of vascular malformation of the lymphatic system characterized by lymphatic vessels which do not connect to the normal lymphatic circulation. The term lymphangioma is outdated and newer research reference the term lymphatic malformation.
Lymphatic malformations can be macrocystic, microcystic, or a combination of the two.[1] Macrocystic have cysts greater than 2 cubic centimetres (0.12 cu in), and microcystic lymphatic malformation have cysts that are smaller than 2 cubic centimetres (0.12 cu in).[2]
These malformations can occur at any age and may involve any part of the body, but 90% occur in children less than 2 years of age and involve the head and neck. These malformations are either congenital or acquired. Congenital lymphangiomas are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as Turner syndrome, although they can also exist in isolation. Lymphangiomas are commonly diagnosed before birth using fetal ultrasonography. Acquired lymphangiomas may result from trauma, inflammation, or lymphatic obstruction.
Most lymphangiomas are benign lesions that result only in a soft, slow-growing, "doughy" mass. Since they have no chance of becoming malignant, lymphangiomas are usually treated for cosmetic reasons only. Rarely, impingement upon critical organs may result in complications, such as respiratory distress when a lymphangioma compresses the airway. Treatment includes aspiration, surgical excision, laser and radiofrequency ablation, and sclerotherapy.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Elluruwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Microcystic lymphatic malformation | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov.