| Lymphocytosis | |
|---|---|
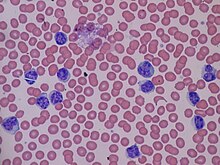 | |
| Lymphocytosis, peripheral blood smear (40x) | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the condition where the proportion of lymphocytes relative to white blood cell count is above the normal range. In adults, absolute lymphocytosis is present when the lymphocyte count is greater than 5000 per microliter (5.0 x 109/L), in older children greater than 7000 per microliter and in infants greater than 9000 per microliter.[1] Lymphocytes normally represent 20% to 40% of circulating white blood cells. When the percentage of lymphocytes exceeds 40%, it is recognized as relative lymphocytosis.
- ^ Miale, John B. Laboratory Medicine: hematology. 5th. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby, 1977.