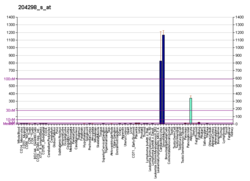
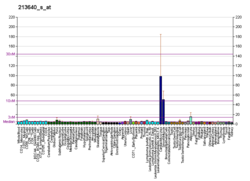
Lysyl oxidase (LOX), also known as protein-lysine 6-oxidase, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the LOX gene.[5][6] It catalyzes the conversion of lysine residues into its aldehyde derivative allysine.[7] Allysine form cross-links in extracellular matrix proteins. Inhibition of lysyl oxidase can cause osteolathyrism, but, at the same time, its upregulation by tumor cells may promote metastasis of the existing tumor, causing it to become malignant and cancerous.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000113083 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024529 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: LOX lysyl oxidase".
- ^ Hämäläinen ER, Jones TA, Sheer D, Taskinen K, Pihlajaniemi T, Kivirikko KI (Nov 1991). "Molecular cloning of human lysyl oxidase and assignment of the gene to chromosome 5q23.3-31.2". Genomics. 11 (3): 508–16. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90057-L. PMID 1685472.
- ^ Requena JR, Levine RL, Stadtman ER (2003). "Recent Advances in the Analysis of Oxidized Proteins". Amino Acids. 25 (3–4): 221–226. doi:10.1007/s00726-003-0012-1. PMID 14661085. S2CID 28837698.