 | |
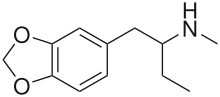
 Chemical structure | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Methylbenzodioxolyl-butanamine; N-Methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine; MBDB; 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-butanphenamine; MDMB; 1,3-Benzodioxolyl-N-methylbutanamine; BDMB; 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-ethylphenylethylamine; 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-desmethyl-α-ethylamphetamine; Eden; Methyl-J |
| Drug class | Serotonin–norepinephrine releasing agent; Empathogen–entactogen |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Duration of action | 4–6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 207.273 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 156 °C (313 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
MBDB, also known as N-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine or as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-ethylphenylethylamine, is an entactogen of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and phenylisobutylamine families related to MDMA.[1][2][3][4] It is known by the street names "Eden" and "Methyl-J".[4]
- ^ Oeri HE (May 2021). "Beyond ecstasy: Alternative entactogens to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine with potential applications in psychotherapy". J Psychopharmacol. 35 (5): 512–536. doi:10.1177/0269881120920420. PMC 8155739. PMID 32909493.
- ^ Aerts LA, Mallaret M, Rigter H (July 2000). "N-methyl-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-butanamine (MBDB): its properties and possible risks". Addict Biol. 5 (3): 269–282. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2000.tb00191.x. PMID 20575841.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
NicholsMarona-LewickaHuang1993was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "MBDB". Erowid Center.