
An MRI pulse sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance.[1]
A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including other specialized MRI configurations such as spectroscopy.[2][3]
Overview table
This table does not include uncommon and experimental sequences.
| Group | Sequence | Abbr. | Physics | Main clinical distinctions | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spin echo | T1 weighted | T1 | Measuring spin–lattice relaxation by using a short repetition time (TR) and echo time (TE). |
Standard foundation and comparison for other sequences |

|
| T2 weighted | T2 | Measuring spin–spin relaxation by using long TR and TE times |
Standard foundation and comparison for other sequences |

| |
| Proton density weighted | PD | Long TR (to reduce T1) and short TE (to minimize T2).[7] | Joint disease and injury.[8]
|

| |
| Gradient echo (GRE) | Steady-state free precession | SSFP | Maintenance of a steady, residual transverse magnetisation over successive cycles.[10] | Creation of cardiac MRI videos (pictured).[10] | 
|
| Effective T2 or "T2-star" |
T2* | Spoiled gradient recalled echo (GRE) with a long echo time and small flip angle[11] | Low signal from hemosiderin deposits (pictured) and hemorrhages.[11] | 
| |
| Susceptibility-weighted | SWI | Spoiled gradient recalled echo (GRE), fully flow compensated, long echo time, combines phase image with magnitude image[12] | Detecting small amounts of hemorrhage (diffuse axonal injury pictured) or calcium.[12] | 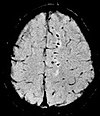
| |
| Inversion recovery | Short tau inversion recovery | STIR | Fat suppression by setting an inversion time where the signal of fat is zero.[13] | High signal in edema, such as in more severe stress fracture.[14] Shin splints pictured: | 
|
| Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery | FLAIR | Fluid suppression by setting an inversion time that nulls fluids | High signal in lacunar infarction, multiple sclerosis (MS) plaques, subarachnoid haemorrhage and meningitis (pictured).[15] | 
| |
| Double inversion recovery | DIR | Simultaneous suppression of cerebrospinal fluid and white matter by two inversion times.[16] | High signal of multiple sclerosis plaques (pictured).[16] | 
| |
| Diffusion weighted (DWI) | Conventional | DWI | Measure of Brownian motion of water molecules.[17] | High signal within minutes of cerebral infarction (pictured).[18] | 
|
| Apparent diffusion coefficient | ADC | Reduced T2 weighting by taking multiple conventional DWI images with different DWI weighting, and the change corresponds to diffusion.[19] | Low signal minutes after cerebral infarction (pictured).[20] | 
| |
| Diffusion tensor | DTI | Mainly tractography (pictured) by an overall greater Brownian motion of water molecules in the directions of nerve fibers.[21] |
|
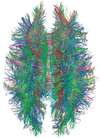
| |
| Perfusion weighted (PWI) | Dynamic susceptibility contrast | DSC | Measures changes over time in susceptibility-induced signal loss due to gadolinium contrast injection.[23] |
|

|
| Arterial spin labelling | ASL | Magnetic labeling of arterial blood below the imaging slab, which subsequently enters the region of interest.[25] It does not need gadolinium contrast.[26] | |||
| Dynamic contrast enhanced | DCE | Measures changes over time in the shortening of the spin–lattice relaxation (T1) induced by a gadolinium contrast bolus.[27] | Faster Gd contrast uptake along with other features is suggestive of malignancy (pictured).[28] | 
| |
| Functional MRI (fMRI) | Blood-oxygen-level dependent imaging | BOLD | Changes in oxygen saturation-dependent magnetism of hemoglobin reflects tissue activity.[29] | Localizing brain activity from performing an assigned task (e.g. talking, moving fingers) before surgery, also used in research of cognition.[30] | 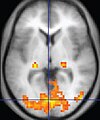
|
| Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and venography | Time-of-flight | TOF | Blood entering the imaged area is not yet magnetically saturated, giving it a much higher signal when using short echo time and flow compensation. | Detection of aneurysm, stenosis, or dissection[31] | 
|
| Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging | PC-MRA | Two gradients with equal magnitude, but opposite direction, are used to encode a phase shift, which is proportional to the velocity of spins.[32] | Detection of aneurysm, stenosis, or dissection (pictured).[31] | 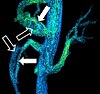 (VIPR) |
- ^ Jones J, Gaillard F. "MRI sequences (overview)". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Marino MA, Helbich T, Baltzer P, Pinker-Domenig K (February 2018). "Multiparametric MRI of the breast: A review". Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 47 (2): 301–315. doi:10.1002/jmri.25790. PMID 28639300. S2CID 206108382.
- ^ Tahmassebi A, Wengert GJ, Helbich TH, Bago-Horvath Z, Alaei S, Bartsch R, et al. (February 2019). "Impact of Machine Learning With Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast for Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Survival Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients". Investigative Radiology. 54 (2): 110–117. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000518. PMC 6310100. PMID 30358693.
- ^ a b c d "Magnetic Resonance Imaging". University of Wisconsin. Archived from the original on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- ^ a b c d Johnson KA. "Basic proton MR imaging. Tissue Signal Characteristics". Harvard Medical School. Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- ^ Henkelman, RM; Hardy, PA; Bishop, JE; Poon, CS; Plewes, DB (September 1992). "Why fat is bright in RARE and fast spin-echo imaging". Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI. 2 (5): 533–40. doi:10.1002/jmri.1880020511. PMID 1392246.
- ^ Graham D, Cloke P, Vosper M (2011-05-31). Principles and Applications of Radiological Physics E-Book (6 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-7020-4614-8.}
- ^ du Plessis V, Jones J. "MRI sequences (overview)". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-01-13.
- ^ Lefevre N, Naouri JF, Herman S, Gerometta A, Klouche S, Bohu Y (2016). "A Current Review of the Meniscus Imaging: Proposition of a Useful Tool for Its Radiologic Analysis". Radiology Research and Practice. 2016: 8329296. doi:10.1155/2016/8329296. PMC 4766355. PMID 27057352.
- ^ a b Luijkx T, Weerakkody Y. "Steady-state free precession MRI". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ a b Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Thomas B, Shroff MM, Haacke EM (2009). "Principles, techniques, and applications of T2*-based MR imaging and its special applications". Radiographics. 29 (5): 1433–49. doi:10.1148/rg.295095034. PMC 2799958. PMID 19755604.
- ^ a b Di Muzio B, Gaillard F. "Susceptibility weighted imaging". Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Sharma R, Taghi Niknejad M. "Short tau inversion recovery". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ Berger F, de Jonge M, Smithuis R, Maas M. "Stress fractures". Radiology Assistant. Radiology Society of the Netherlands. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ Hacking C, Taghi Niknejad M, et al. "Fluid attenuation inversion recoveryg". radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 2015-12-03.
- ^ a b Di Muzio B, Abd Rabou A. "Double inversion recovery sequence". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ Lee M, Bashir U. "Diffusion weighted imaging". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ Weerakkody Y, Gaillard F. "Ischaemic stroke". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Hammer M. "MRI Physics: Diffusion-Weighted Imaging". XRayPhysics. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ An H, Ford AL, Vo K, Powers WJ, Lee JM, Lin W (May 2011). "Signal evolution and infarction risk for apparent diffusion coefficient lesions in acute ischemic stroke are both time- and perfusion-dependent". Stroke. 42 (5): 1276–81. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.610501. PMC 3384724. PMID 21454821.
- ^ a b Smith D, Bashir U. "Diffusion tensor imaging". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
- ^ Chua TC, Wen W, Slavin MJ, Sachdev PS (February 2008). "Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a review". Current Opinion in Neurology. 21 (1): 83–92. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f4594b. PMID 18180656. S2CID 24731783.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR perfusion". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-14.
- ^ Chen F, Ni YC (March 2012). "Magnetic resonance diffusion-perfusion mismatch in acute ischemic stroke: An update". World Journal of Radiology. 4 (3): 63–74. doi:10.4329/wjr.v4.i3.63. PMC 3314930. PMID 22468186.
- ^ "Arterial spin labeling". University of Michigan. Retrieved 2017-10-27.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Arterial spin labelling (ASL) MR perfusion". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MR perfusion". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Turnbull LW (January 2009). "Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the diagnosis and management of breast cancer". NMR in Biomedicine. 22 (1): 28–39. doi:10.1002/nbm.1273. PMID 18654999. S2CID 5305422.
- ^ Chou Ih. "Milestone 19: (1990) Functional MRI". Nature. Retrieved 9 August 2013.
- ^ Luijkx T, Gaillard F. "Functional MRI". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-16.
- ^ a b "Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)". Johns Hopkins Hospital. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ^ Keshavamurthy J, Ballinger R et al. "Phase contrast imaging". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2017-10-15.