| Maize | |
|---|---|
| |
| Includes male and female flowers | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Subfamily: | Panicoideae |
| Genus: | Zea |
| Species: | Z. mays
|
| Binomial name | |
| Zea mays | |
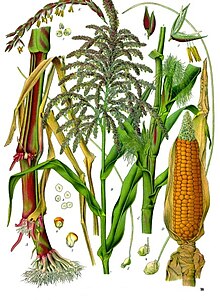
Maize /meɪz/ (Zea mays), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors.
Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sweet corn are grown for human consumption, while field corn varieties are used for animal feed, for uses such as cornmeal or masa, corn starch, corn syrup, pressing into corn oil, alcoholic beverages like bourbon whiskey, and as chemical feedstocks including ethanol and other biofuels.
Maize is cultivated throughout the world; a greater weight of maize is produced each year than any other grain. In 2020, world production was 1.1 billion tonnes. It is afflicted by many pests and diseases; two major insect pests, European corn borer and corn rootworms, have each caused annual losses of a billion dollars in the US. Modern plant breeding has greatly increased output and qualities such as nutrition, drought tolerance, and tolerance of pests and diseases. Much maize is now genetically modified.
As a food, maize is used to make a wide variety of dishes including Mexican tortillas and tamales, Italian polenta, and American hominy grits. Maize protein is low in some essential amino acids, and the niacin it contains only becomes available if freed by alkali treatment. In Mesoamerica, maize is deified as a maize god and depicted in sculptures.
- ^ Contreras, A.; Ruíz Corral, J. A.; Menjívar, J.; Aragón Cuevas, F.; González Ledesma, M.; Sánchez, J. J. (2019). "Zea mays". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: E.T77726273A77726310. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T77726273A77726310.en.
