Malla Republic | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 7th century BCE–c. 4th century BCE | |||||||
 Malla among the Gaṇasaṅghas | |||||||
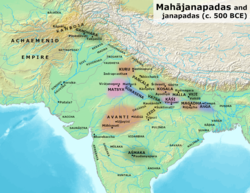 Malla, Vajji (the dependencies of Licchavi within the Vajjika League), and other Mahajanapadas in the Post Vedic period | |||||||
| Status | Republic of the Vajjika League | ||||||
| Capital | Kusinārā Pāvā | ||||||
| Common languages | Prakrit | ||||||
| Religion | Historical Vedic religion Buddhism Jainism | ||||||
| Government | Aristocratic Republic | ||||||
| Gaṇa Mukhya | |||||||
| Legislature | Sabhā | ||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||
• Established | c. 7th century BCE | ||||||
• Disestablished | c. 4th century BCE | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||
Malla (Prakrit: 𑀫𑀮𑁆𑀮𑀈 Mallaī; Pali: Malla; Sanskrit: मल्ल Malla) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern Indian subcontinent whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Malla, the Mallakas, were divided into two branches, each organised into a gaṇasaṅgha (an aristocratic oligarchic republic), presently referred to as the Malla Republics, which were part of the larger Vajjika League.[1]
- ^ Sharma 1968, p. 169-181.