 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /məˈrɒpɪtænt/ mə-ROP-i-tant |
| Trade names | Cerenia, Prevomax, Vetemex |
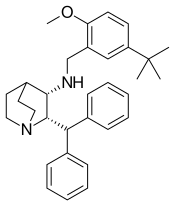
| Other names | (2S,3S)-2-Benzhydryl-N-(5-tert-butyl-2-methoxybenzyl) quinuclidin-3-amine, maropitant citrate (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, subcutaneous, Intravenous transdermal |
| Drug class | Antiemetic |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 20–30% dogs, 50% cats SQ: 90% (both) |
| Protein binding | 99.5% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A12 and CYP2D15) |
| Metabolites | CJ-18,518 |
| Elimination half-life | 6–8 hours (SQ) |
| Duration of action | 24 hours (SQ) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H40N2O |
| Molar mass | 468.685 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Maropitant (INN;[2] brand name: Cerenia, used as maropitant citrate (USAN), is a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist developed by Zoetis specifically for the treatment of motion sickness and vomiting in dogs. It was approved by the FDA in 2007, for use in dogs[3][4] and in 2012, for cats.[5]
Maropitant mildly reduces intra-procedural inhaled anesthesia dose requirements but does not confer analgesia itself.[6] [7]
- ^ "Cerenia EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 5 October 2006. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 52" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2004. pp. 254–255. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ^ "Cerenia (maropitant citrate) Injectable Solution, Dogs" (PDF). Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 19 April 2011.
- ^ Package Insert for Cerenia at Pfizer Animal Health (full detailed drug information)
- ^ Riviere JE, Papich MG (2017). "Maropitant". Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. John Wiley & Sons. p. 2828. ISBN 978-1-118-85588-1.
- ^ Boscan P, Monnet E, Mama K, Twedt DC, Congdon J, Steffey EP (December 2011). "Effect of maropitant, a neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist, on anesthetic requirements during noxious visceral stimulation of the ovary in dogs". American Journal of Veterinary Research. 72 (12): 1576–1579. doi:10.2460/ajvr.72.12.1576. PMID 22126683.
- ^ Kinobe RT, Miyake Y (2020). "Evaluating the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of maropitant: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Veterinary Journal. 259–260: 105471. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2020.105471. PMID 32553233.