| History of India |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
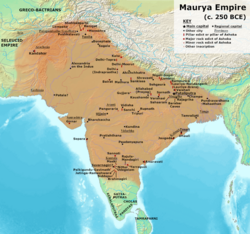
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia based in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya, who overthrew the Nanda Empire in 322 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE.[g] The primary sources for the written records of the Mauryan times are the Arthashastra, a work first discovered in the early 20th century,[11] and previously attributed to Kautilya, but now thought to be composed by multiple authors in the first centuries of the common era;[h] partial records of the lost history of Megasthenes in Roman texts of several centuries later;[12] and the Edicts of Ashoka, which were first read in the modern era by James Prinsep after he had deciphered the Brahmi and Kharoshthi scripts in 1838.[13]
Through military conquests and diplomatic treaties, Chandragupta extended his suzerainty as far westward as Afghanistan below the Hindu Kush and as far south as the northern Deccan;[14] however, beyond the core Magadha area, the prevailing levels of technology and infrastructure limited how deeply his rule could penetrate society.[15][16] During the rule of Chandragupta's grandson, Ashoka (ca. 268–232 BCE), the empire briefly controlled the major urban hubs and arteries of the subcontinent excepting the deep south.[g] Thereafter, the empire declined for about 50 years until the last ruler was assassinated by Pushyamitra Shunga.
The Mauryan economy was helped by the earlier rise of Buddhism and Jainism—creeds that promoted nonviolence, proscribed ostentation, or superfluous sacrifices and rituals, and reduced the costs of economic transactions; by coinage that increased economic accommodation in the region; and by the use of writing, which might have boosted more intricate business dealings. Despite profitable settled agriculture in the fertile eastern Gangetic plain, these factors helped maritime and river-borne trade, which were essential for acquiring goods for consumption as well as metals of high economic value.[17] The Mauryan capital was located in Pataliputra (modern Patna). Outside this imperial centre, the empire's geographical extent was dependent on the loyalty of military commanders who controlled the armed cities scattered within it.[18][19][a] The Maurya dynasty built a road, a chiefly winter-time road—the Uttarapath—which connected eastern Afghanistan to their capital Patliputra during the time of year when the water levels in the intersecting rivers were low and they could be easily forded.[20] After the Kalinga War in which Ashoka's troops visited much violence on the region, Ashoka embraced Buddhism and promoted its tenets in edicts scattered in clusters around South Asia.[a] He sponsored Buddhist missionaries to Sri Lanka, northwest India, and Central Asia and played a salient role in Buddhism becoming a world religion.[21]
The population of South Asia during the Mauryan period has been estimated to be between 15 and 30 million.[22] The empire's period of dominion was marked by exceptional creativity in art, architecture, inscriptions and produced texts,[23] but also by the consolidation of caste in the Gangetic plain, and the declining rights of women in the mainstream Indo-Aryan speaking regions of India.[24] Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW). The Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath is the State Emblem of the Republic of India, and the 24-pointed Buddhist Wheel of Dharma on the capital's drum-shaped abacus, is the central feature of India's national flag.[25]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Nath Sen 1999, p. 164, (215) 217.
- ^ Smith 1981, p. 99.
- ^ Dalrymple 2009.
- ^ Keay 1981, p. 85-86.
- ^ a b Bronkhorst 2020, p. 68.
- ^ a b Long 2020, p. 255.
- ^ Boyce & Grenet 1991, p. 149.
- ^ Avari 2007, p. 188-189.
- ^ Taagepera 1979, p. 132.
- ^ Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 223. ISSN 1076-156X. Archived from the original on 20 May 2019. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ^ Stein & Arnold (2010, p. 73): "... another source that enjoyed high standing as a description of the early Mauryan state was the Arthashastra, a treatise on power discovered in the early twentieth century."
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
coningham-young-p451-megastheneswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
michon-2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ludden (2013, p. 47): "IMPERIAL BHARAT The Mauryas defined an ancient territory called Bharat. Marching along old trade routes, the empire acquired the geometrical shape of a tall triangle with a broad base, with its apex in Magadha. One long northern leg ran west up the Ganga, across Punjab, into the Hindu Kush; and one long leg ran south-west from Pataliputra, up the Son river valley, down the Narmada River into Berar, Maharashtra, and Gujarat. The broad base spanned Punjab, the Indus, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and western Maharashtra. The northwestern frontier revolved around Gandhara and Kashmir; the south-western frontier around Nasika, now Nasik, in Maharashtra. North of Kashmir and west of the Khyber Pass, Greek dynasties held sway. South of Nasika, the Mauryan presence consisted primarily of diplomatic missions."
- ^ Fisher (2018, p. 72): "Chandragupta’s many military and diplomatic conquests extended his overlordship further than any previous Indian ruler: from Afghanistan to Bengal and from the Himalayas down into the northern Deccan. But his administration lacked the technology and infrastructure to penetrate very deeply into society outside of Magadha."
- ^ Stein & Arnold (2010, p. 73): "In 305 BCE one of his successors attempted a reinvasion but was so fiercely resisted that he was forced to conclude a treaty with Chandragupta that accepted the latter’s sovereignty south of the Hindu Kush range."
- ^ Roy (2012a, p. 28): "This period is noted for three important changes. One change was the rise of religions that advocated nonviolence, thereby reducing sacrifices and expensive rituals. The emphasis on a frugal lifestyle and peaceful neighborly relations suited the mercantile temperament. Not surprisingly, merchants were the principal sponsors of these religions. Settlement sites have been found in the middle-Ganges plains for this earliest period of known commerce that indicate the presence of long-distance trade. A second change was the introduction of coinage in the sixth century BCE, which promoted regional monetary integration. The third change was the increasing use of writing, which may have indirectly helped long-distance and complex economic transactions.5 This process of change was centered in the eastern Gangetic plains, where settled agriculture had given rise to powerful landed communities yet where access to the sea and to river-borne trade remained the principal means of procuring precious metals and consumption goods. States, therefore, chose to sponsor merchants and the religion of the merchants, Buddhism. The Mauryan Empire revealed a combination of all of these elements: commerce, religion, agriculture, and coinage."
- ^ Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. xii, 448.
- ^ Thapar 1990, p. 384.
- ^ Iori, Elisa (2023). "Releasing Urban Religion beyond the City Wall: The Spatial Capital of Early Buddhist Monasticism in NW South Asia". Numen. 70 (2–3): 184–219. doi:10.1163/15685276-20231691.
At the end of the farming year when the land was free of crops (end of October–April) and the water level low, it was the time for maintenance activities (e.g., clearing of wells and water infrastructure) and the time when manpower could be invested in other production and building activities both in rural and urban contexts. But above all, this was the time for movement and trade. The uttarāpatha, that is the main road linking eastern Afghanistan to India through the cities of Kabul, Charsadda, and Taxila down to Patna, is indeed a winter road typically used when local rivers (Kabul, Indus, and the rivers of Punjab) are at their lowest levels, so that they can be easily forded (Olivieri 2020: 645–646).
- ^ Kulke & Rothermund 2004, p. 67.
- ^ Dyson 2018, p. 24 Quote: "Yet Sumit Guha considers that 20 million is an upper limit. This is because the demographic growth experienced in core areas is likely to have been less than that experienced in areas that were more lightly settled in the early historic period. The position taken here is that the population in Mauryan times (320–220 BCE) was between 15 and 30 million—although it may have been a little more, or it may have been a little less."
- ^ Ludden (2013, pp. 28–29): "A creative explosion in all the arts was a most remarkable feature of this ancient transformation, a permanent cultural legacy. Mauryan territory was created in its day by awesome armies and dreadful war, but future generations would cherish its beautiful pillars, inscriptions, coins, sculptures, buildings, ceremonies, and texts, particularly later Buddhist writers."
- ^ Dyson 2018, p. 19 Quote: "Accordingly, as tribal societies were encountered by the expanding Indo-Aryan societies, so the evolving caste system provided a framework within which—invariably at a low level—tribal people could be placed. For example, by the time of the Mauryan Empire (c.320–230 bce) the caste system was quite well established and the Aranyachará (i.e. forest people) were grouped with the most despised castes. ... The evolution of Indo-Aryan society in the centuries before c.200 bce not only saw increased segregation with respect to caste, it also seems to have seen increased differentiation with respect to gender. ... Therefore, by the time of the Mauryan Empire the position of women in mainstream Indo-Aryan society seems to have deteriorated. Customs such as child marriage and dowry were becoming entrenched; and a young women's purpose in life was to provide sons for the male lineage into which she married. To quote the Arthashāstra: 'wives are there for having sons'. Practices such as female infanticide and the neglect of young girls were possibly also developing at this time, especially among higher caste people. Further, due to the increasingly hierarchical nature of the society, marriage was possibly becoming an even more crucial institution for childbearing and the formalization of relationships between groups. In turn, this may have contributed to the growth of increasingly instrumental attitudes towards women and girls (who moved home at marriage). It is important to note that, in all likelihood, these developments did not affect people living in large parts of the subcontinent—such as those in the south, and tribal communities inhabiting the forested hill and plateau areas of central and eastern India. That said, these deleterious features have continued to blight Indo-Aryan speaking areas of the subcontinent until the present day."
- ^ Vajpeyi, Ananya (2012). Righteous Republic: The Political Foundations of Modern India. Cambridge MA and London: Harvard University Press. pp. 188–189. ISBN 978-0-674-04895-9.