| Mean arterial pressure | |
|---|---|
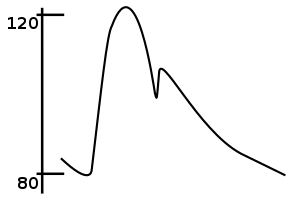 Representation of the arterial pressure waveform over one cardiac cycle. The notch in the curve is associated with closing of the aortic valve. | |
| MeSH | D062186 |
In medicine, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is an average calculated blood pressure in an individual during a single cardiac cycle.[1] Although methods of estimating MAP vary, a common calculation is to take one-third of the pulse pressure (the difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures), and add that amount to the diastolic pressure.[2][3] A normal MAP is about 90 mmHg.[4]
Mean arterial pressure = diastolic blood pressure + (systolic blood pressure - diastolic blood pressure)/3
MAP is altered by cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance.[5] It is used clinically to estimate the risk of cardiovascular diseases, where a MAP of 90 mmHg or less is low risk, and a MAP of greater than 96 mmHg represents "stage one hypertension" with increased risk.[3][4]
- ^ Zheng L, Sun Z, Li J, Zhang R, Zhang X, Liu S, et al. (July 2008). "Pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure in relation to ischemic stroke among patients with uncontrolled hypertension in rural areas of China". Stroke. 39 (7): 1932–1937. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.510677. PMID 18451345.
- ^ "Calculating the mean arterial pressure (MAP)". Nursing Center. 8 December 2011.
- ^ a b Melgarejo JD, Yang WY, Thijs L, et al. (January 2021). "Association of Fatal and Nonfatal Cardiovascular Outcomes With 24-Hour Mean Arterial Pressure". Hypertension. 77 (1): 39–48. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14929. PMC 7720872. PMID 33296250.
- ^ a b "Understanding Blood Pressure Readings". American Heart Association. 2023. Retrieved 3 June 2023.
- ^ DeMers D, Wachs D (2022). "Physiology, Mean Arterial Pressure". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30855814. Retrieved 2022-05-22.