
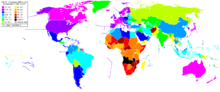
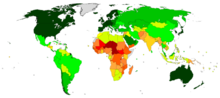

- Above 50
- Between 45 and 50
- Between 40 and 45
- Between 35 and 40
- Between 30 and 35
- Below 30
- No data


Poverty is measured in different ways by different bodies, both governmental and nongovernmental. Measurements can be absolute, which references a single standard, or relative, which is dependent on context. Poverty is widely understood to be multidimensional, comprising social, natural and economic factors situated within wider socio-political processes.
The main poverty line used in the OECD and the European Union is a relative poverty measure based on 60% of the median household income. The United States uses an absolute poverty measure based on the U.S. Department of Agriculture's "economy food plan", adjusted for inflation. The World Bank also defines poverty in absolute terms. It defines extreme poverty as living on less than US$1.90 per day.[2] (PPP), and moderate poverty as less than $3.10 a day.
It has been estimated that in 2008, 1.4 billion people had consumption levels below US$1.25 a day and 2.7 billion lived on less than $2 a day.[needs update]
- ^ "Gini index (World Bank estimate)". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 2022-04-23. Retrieved 2022-04-23.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
worldbank2008was invoked but never defined (see the help page).