| Meles Temporal range: Early Pleistocene to present
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Meles meles, M. leucurus, and M. anakuma. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Subfamily: | Melinae |
| Genus: | Meles Brisson, 1762 |
| Type species | |
| [Ursus] meles Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Species | |
| |
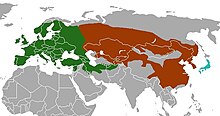
| Ranges of the four (considered three in map) extant species | |
Meles is a genus of badgers containing four living species known as Eurasian badgers, the Japanese badger (Meles anakuma), Asian badger (Meles leucurus), Caucasian badger (Meles canescens) and European badger (Meles meles).[2][3] In an older categorization, they were seen as a single species with three subspecies (Meles meles anakuma, Meles meles leucurus and Meles meles meles). There are also several extinct members of the genus. They are members of the subfamily Melinae of the weasel family, Mustelidae.[4][5][6]
- ^ Madurell-Malapiera, J.; et al. (2011). "The taxonomic status of European Plio-Pleistocene badgers". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (4): 885–894. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.589484. S2CID 85176011.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 611–612. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ "ASM Mammal Diversity Database". www.mammaldiversity.org. Retrieved 2021-06-25.
- ^ Koepfli KP, Deere KA, Slater GJ, Begg C, Begg K, Grassman L, Lucherini M, Veron G, Wayne RK (February 2008). "Multigene phylogeny of the Mustelidae: Resolving relationships, tempo and biogeographic history of a mammalian adaptive radiation". BMC Biology. 6: 10. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-6-10. PMC 2276185. PMID 18275614.
- ^ Yu L, Peng D, Liu J, Luan P, Liang L, Lee H, Lee M, Ryder OA, Zhang Y (2011). "On the phylogeny of Mustelidae subfamilies: analysis of seventeen nuclear non-coding loci and mitochondrial complete genomes". BMC Evol Biol. 11 (1): 92. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-92. PMC 3088541. PMID 21477367.
- ^ Law, C. J.; Slater, G. J.; Mehta, R. S. (2018-01-01). "Lineage Diversity and Size Disparity in Musteloidea: Testing Patterns of Adaptive Radiation Using Molecular and Fossil-Based Methods". Systematic Biology. 67 (1): 127–144. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syx047. PMID 28472434.