 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Buronil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intramuscular injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 87% (IM), 54% (Oral via syrup), 65% (Oral, tablet)[1] |
| Protein binding | 50% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3–4 hours (oral)[1] 6 hours (IM) |
| Excretion | Renal (70% as metabolites, 5.5–10.4% as unchanged drug)[1][2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.027 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
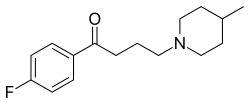
| Formula | C16H22FNO |
| Molar mass | 263.356 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Melperone (Bunil (PT), Buronil (AT, BE, CZ, DK, FI†, NL†, NO†, SE), Eunerpan (DE))[3] is an atypical antipsychotic of the butyrophenone chemical class, making it structurally related to the typical antipsychotic haloperidol. It first entered clinical use in 1960s.[4]
- ^ a b c Borgström L, Larsson H, Molander L (1982). "Pharmacokinetics of parenteral and oral melperone in man". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 23 (2): 173–6. doi:10.1007/BF00545974. PMID 7140807. S2CID 36697288.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
I1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
MDwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Auditwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).