 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Meptid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Dependence liability | Low |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous |
| Drug class | Opioid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | The peak analgesic effect is seen within 30–60 minutes and lasts about 3–4 hours |
| Elimination half-life | Half-life (1.4–4 hours) |
| Excretion | The drug is rapidly metabolized to the glucuronide, and mostly excreted in the urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.718 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H23NO |
| Molar mass | 233.355 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
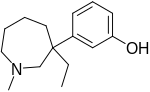
Meptazinol, sold under the brand name Meptid, is an opioid analgesic developed by Wyeth in the 1970s.[1] Indications for use in moderate to severe pain, most commonly used to treat pain in obstetrics (childbirth).
Meptazinol is a 3-phenylazepane derivative, whereas the other phenazepanes like ethoheptazine and proheptazine are 4-phenylazepanes.
A partial μ-opioid receptor agonist, its mixed agonist/antagonist activity affords it a lower risk of dependence and abuse than full μ agonists like morphine. Meptazinol exhibits not only a short onset of action, but also a shorter duration of action relative to other opioids such as morphine, pentazocine, or buprenorphine.[2]
- ^ US patent 4197239, Cavalla JF, Shepherd RG, White AC, "Hexahydroazepine, Piperidine and Pyrrolidine Derivatives", issued 1980-04-08, assigned to Wyeth
- ^ Holmes B, Ward A (1985). "Meptazinol. A Review of its Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy". Drugs. 30 (4): 285–312. doi:10.2165/00003495-198530040-00001. PMID 2998723. S2CID 208818234.