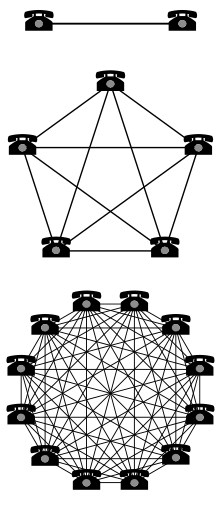
Metcalfe's law states that the financial value or influence of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system (n2). The law is named after Robert Metcalfe and was first proposed in 1980, albeit not in terms of users, but rather of "compatible communicating devices" (e.g., fax machines, telephones).[1] It later became associated with users on the Ethernet after a September 1993 Forbes article by George Gilder.[2]
- ^ Simeonov, Simeon (26 July 2006). "Metcalfe's Law: more misunderstood than wrong?". HighContrast: Innovation & venture capital in the post-broadband era.
- ^ Shapiro, Carl; Varian, Hal R. (1999). Information Rules. Harvard Business Press. ISBN 9780875848631.