| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
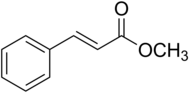
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Methyl cinnamate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.813 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 162.188 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.092 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 34–38 °C (93–100 °F; 307–311 K) |
| Boiling point | 261–262 °C (502–504 °F; 534–535 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P261, P272, P280, P302+P352, P321, P333+P313, P363, P501 | |
| Flash point | > 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl cinnamate is the methyl ester of cinnamic acid and is a white or transparent solid with a strong, aromatic odor. It is found naturally in a variety of plants, including in fruits, like strawberry, and some culinary spices, such as Sichuan pepper and some varieties of basil.[4] Eucalyptus olida has the highest known concentrations of methyl cinnamate (98%) with a 2–6% fresh weight yield in the leaf and twigs.[5]
Methyl cinnamate is used in the flavor and perfume industries. The flavor is fruity and strawberry-like; and the odor is sweet, balsamic with fruity odor, reminiscent of cinnamon and strawberry.[1]
It is known to attract males of various orchid bees, such as Aglae caerulea.[6]

- ^ a b Methyl cinnamate, at goodscents.com
- ^ Methyl cinnamate, at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ "Methyl cinnamate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Viña, Amparo; Murillo, Elizabeth (2003). "Essential oil composition from twelve varieties of basil (Ocimum spp) grown in Colombia". Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society. 14 (5): 744–9. doi:10.1590/S0103-50532003000500008.
- ^ Boland DJ, Brophy JJ, House APN (1991). Eucalyptus Leaf Oils. ISBN 978-0-909605-69-8.
- ^ Williams, N.H.; Whitten, W.M. (1983). "Orchid floral fragrances and male euglossine bees: methods and advances in the last sesquidecade". Biol. Bull. 164 (3): 355–395. doi:10.2307/1541248. JSTOR 1541248.